Uranium: Mining, Uses, History
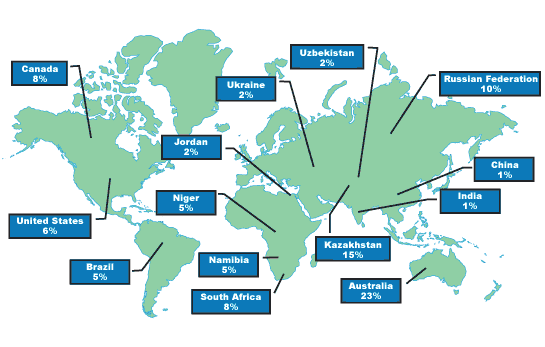
Locations Large deposits of Uranium in the U.S are found in New Mexico, Colorado, Texas, Utah, and Wyoming. Most of Canada’s Uranium comes from the province of Saskatchewan. There is a lot of Uranium in the oceans but we do not have the technology to mine it at a cheap cost. Mining When uranium is…