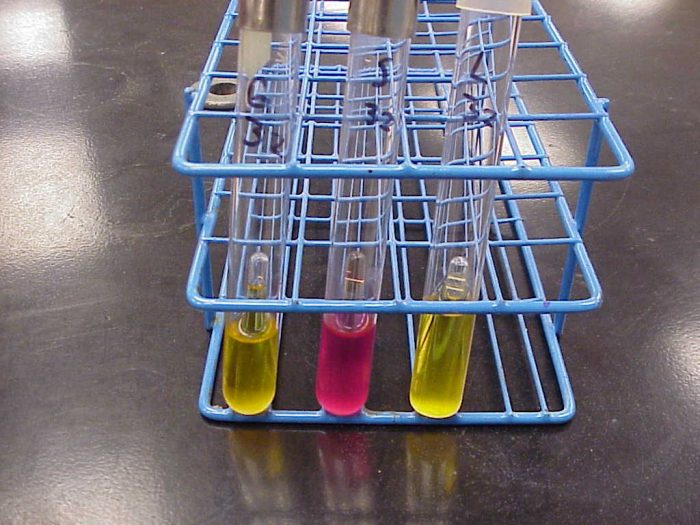
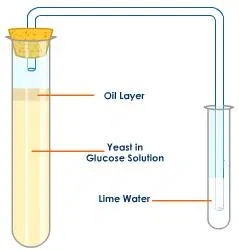
Fermentation of Glucose by Yeast: Lab Explained
Introduction Glucose → Ethanol + Carbon dioxide In the absence of oxygen, enzymes from microorganisms break down sugars through the chemical process called fermentation. Because they possess distinctive sets of metabolic genes, microorganisms like bacteria and fungi can develop enzymes that can break down various kinds of sugar compounds. Therefore, the flavor of fermented food…