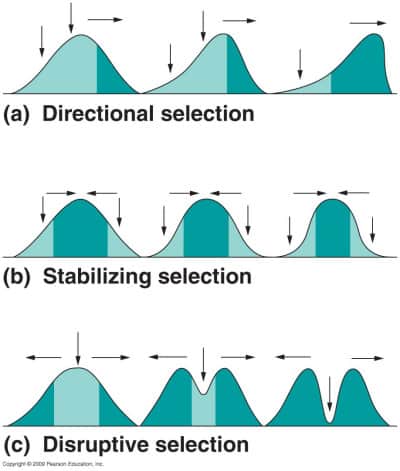
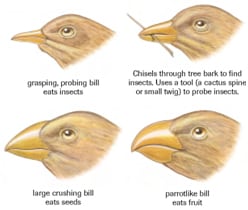
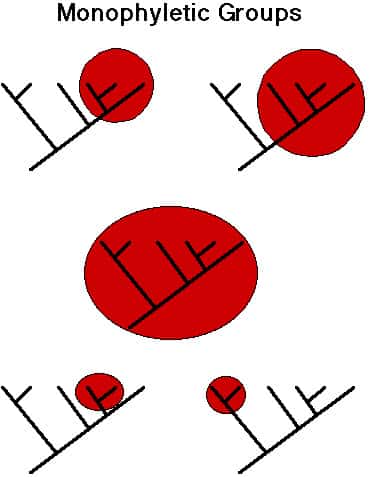
Origins of Music: History, Evolution & Cognition
One of thing things that is common to all of mankind and has been for all of recorded history is the presence of musical ability and expression. Music has transcended throughout every era and every culture and has been constantly changing and evolving alongside with humans. It has played such a significant role in the…