Carbohydrates are the first nutrient most organisms catabolise for energy, however, living things must metabolize other energy-rich nutrients to obtain energy in times of starvation
Protein Catabolism
– first digested into amino acids
– amino groups are removed (deamination; amino group à ammonia [NH3])
– remaining portion of amino acid converted into various components of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle
– the type of amino acid determines the point of entry into these metabolic pathways,
– For example, leucine is converted into acetyl-CoA, alanine is converted into pyruvate
Lipid Catabolism
– first triglycerides are digested into glycerol and fatty acids
– glycerol may be converted into glucose (glucaoneogenesis), or it may be changed into DHAP or G3P à fed into glycolysis
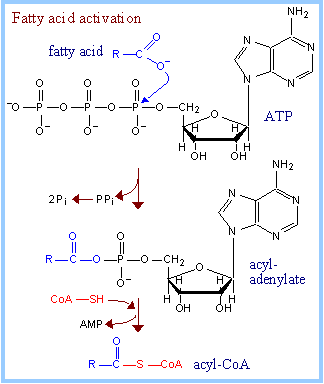
– fatty acids transported to mitochondria (b-oxidation)
– b-oxidation is the removal of two-carbon acetyl groups, starting at the carboxyl end
– acetyl groups combine with coenzyme A to form acetyl-CoA à enter the Krebs cycle
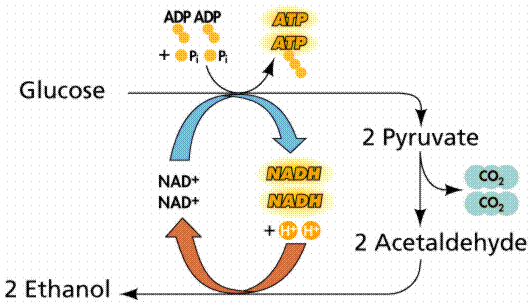
Ethanol Fermentation
– allows NAD+ to be recycled and glycolysis to continue
Lactic Acid Fermentation
– allows NAD+ to be recycled and glycolysis to continue
– lactate in muscle tissue causes stiffness, soreness and fatigue
– lactate is oxidized back to pyruvate, which then goes through the Krebs cycle when vigorous activity ceases


I have to say that for the past few of hours i have been hooked by the impressive articles on this website. Keep up the great work.