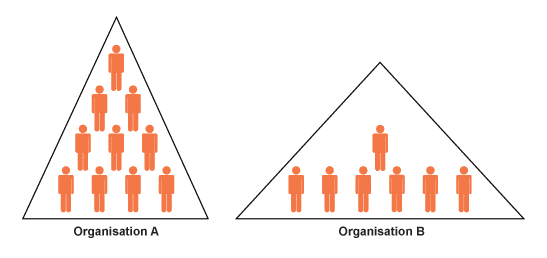
Organizational Structure: Flat and Tall Structure
Define Organizational Structure An organizational structure is a system of how certain activities are directed down in order to accomplish the goal or task of a certain organization. The organizational structure is a hierarchy which identifies the job and function of each level. Flat Structure One characteristic of a Flat Structure is that it has…