Mumps is a disease caused by a virus and occurs only in human beings. Mumps is found all over the world. Mumps is a contagious disease when the salivary glands, on one or both sides of the jaw, swells. Mumps usually occurs in school age children, but young adults may catch the disease. Everyone born before1957 has already had mumps.
After one attack of mumps, you will have lifelong immunity. The mumps virus is spread by contact of another person’s discharge from the 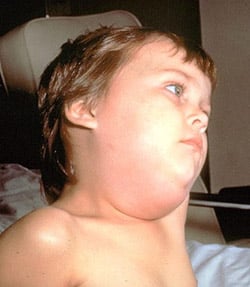 nose or mouth. The virus is present in these discharges from six days before symptoms to nine days after the glands begin to swell. The virus will then incubate for two to three weeks before symptoms appear.
nose or mouth. The virus is present in these discharges from six days before symptoms to nine days after the glands begin to swell. The virus will then incubate for two to three weeks before symptoms appear.
Symptoms include headaches, jaw being painful and tender to the touch, fever, and difficulty swallowing. The swelling usually disappears after seven to ten days. Some complications include deafness (usually only in one ear), arthritis, meningitis (inflammation of brain membranes) and pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas). One of every four male adults with the virus will develop orchtis, which is inflammation of the testes. Sometimes females will have inflammation of the ovaries. Extremely rare cases will result in sterility. Mumps is diagnosed by symptoms, but a blood, urine or saliva test can confirm that you have the virus. Treatment of the virus includes diet of soft foods, bed rest, and pain relievers. The mumps vaccine is given to children that are about twelve months old. The vaccine is usually combined with measles and rubella vaccines, which is called the MMR vaccine.
