Premature babies, otherwise known as preterm babies, or preemies, are babies that are born earlier than the full-term of thirty-eight to forty-two weeks of pregnancy. These babies are generally born between the twentieth and thirty-eighth week. Almost 250,000 babies, nearly seven percent of newborns, are premature(Golant 4). Prematurity, even with all the advances in technology, is still a major cause of fetal and neonatal death.
Actually, around seventy-five percent of prenatal deaths are due to a number of problems associated with prematurity(Freeman 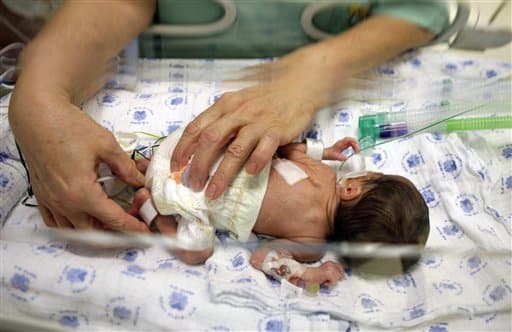 232). Premature babies are very weak and defenseless, and need to be hospitalized. One reason for this is that a baby may become startled into shock by a loud sound or even bright light. This occurs because many babies have fully-developed senses and underdeveloped organs, which may become a problem, since the brain may not be developed well enough to be able to distinguish these different senses, which causes the baby to panic and lose control of its actions. The main underdeveloped parts of a premature baby are its organs, chiefly the lungs and the brain. The lungs are developed in the last few weeks of pregnancy, and if the child is born before the thirty sixth week, he/she may require some special attention. Usually, the child is monitored closely for the first few weeks of its life, in order to make sure there is no problems with the breathing or any other function of its body. The premature baby will probably need supplemental oxygen to help it through the early stages, but rarely will it need an actual respirator or other life-supporting device on a full- time twenty four hour basis. In fact, giving the baby too much oxygen may complicate problems, such as damages to the eyes. This is caused by a over-abundance of oxygen in the blood stream, which in turn causes the blood vessels of the eye to expand, damaging the eye. This problem is one of the main concerns when bearing a pre-term baby versus a full-term baby.
232). Premature babies are very weak and defenseless, and need to be hospitalized. One reason for this is that a baby may become startled into shock by a loud sound or even bright light. This occurs because many babies have fully-developed senses and underdeveloped organs, which may become a problem, since the brain may not be developed well enough to be able to distinguish these different senses, which causes the baby to panic and lose control of its actions. The main underdeveloped parts of a premature baby are its organs, chiefly the lungs and the brain. The lungs are developed in the last few weeks of pregnancy, and if the child is born before the thirty sixth week, he/she may require some special attention. Usually, the child is monitored closely for the first few weeks of its life, in order to make sure there is no problems with the breathing or any other function of its body. The premature baby will probably need supplemental oxygen to help it through the early stages, but rarely will it need an actual respirator or other life-supporting device on a full- time twenty four hour basis. In fact, giving the baby too much oxygen may complicate problems, such as damages to the eyes. This is caused by a over-abundance of oxygen in the blood stream, which in turn causes the blood vessels of the eye to expand, damaging the eye. This problem is one of the main concerns when bearing a pre-term baby versus a full-term baby.
Another difference, probably the most noticeable one, is the size and weight of the baby. A preemie will look thin and helpless, and will also have transparent skin. Blood vessels, veins and bones are sometimes visible through the skin of these babies. This is because the skin of a premature baby is very fragile and tender and can be bruised or broken very easily by a slight amount of pressure. For this reason, many preemies, especially early preemies, are better off not wearing clothing or diapers. Not wearing clothing helps make it easier for the doctor to work with the baby and keep the skin’s stress levels to a minimum. Even though the parents may want to hold and cuddle their baby, it is best for the child and the parents if they keep to a minimum the handling of a preemie.
Doctors are trying to figure out ways to prevent premature labor from occurring. Through a drug called Ritodrive, doctors have been quite successful in prolonging the pregnancy until the thirty-sixth week(Griesemer 15). Although successful in many cases, doctors are still very skeptical on whether or not women should take any form of drugs while they are pregnant. In the past, there was a belief that the placenta protects the unborn baby from all drugs, bur just recently studies have shown that many drugs can be passed from the mother to the child. Another reason which drugs are not regularly administered to upcoming mothers is that it is very difficult to determine how drugs will actually act on the fetus, since test results can vary so differently from person to person, and also because these results are very unpredictable. For this reason, women are rarely prescribed drugs while pregnant, unless when needed or under the care and supervision of their doctor.
Caring for a premature baby can be very tough for parents at times. Since they are urged not to handle the baby much, it makes it very hard for the baby to receive much attention, and also for the parent to see the baby as often as s/he wants to. Feeding a preemie may be a very difficult and cumbersome task. Some preterm babies are fed through an umbilical artery catheter, a tube placed through the navel, or by an intravenous placed through a vein in the baby’s head or scalp. This IV contains a solution with the nutrients the baby needs for survival. More mature preemies may be fed by formula, or even breast milk. Breast milk is preferred, if the baby has developed good enough sucking skills, another skill developed late in pregnancy, and also if the baby’s body is functional enough to tolerate the milk. Some advantages of breast milk over formula are that breast milk can improve growth, provide antibodies against infection, stimulate faster nerve growth, and help regulate heartbeat and breathing patterns through sucking, making the flow of oxygen more even and efficient.
Heart problems are another common problem among prematurely born babies. The most common problem is that blood might circulate 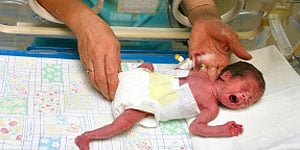 through the body, but without passage through the lungs. This happens while the baby is in the fetus, and continues until about the thirty-sixth week when the lungs are almost fully functional. Recently, a drug has been developed that can be used as a substitute to the old method of surgery that was used to combat this problem in most cases.
through the body, but without passage through the lungs. This happens while the baby is in the fetus, and continues until about the thirty-sixth week when the lungs are almost fully functional. Recently, a drug has been developed that can be used as a substitute to the old method of surgery that was used to combat this problem in most cases.
The causes for premature birth is generally an underdeveloped placenta. One thing that is known to have an affect on this is cigarette smoke, which lowers the oxygen supply to the placenta. Drinking alcohol in large quantities and smoking marijuana and doing other drugs also increases the risk for having a premature baby. Having preterm babies is not an inherent trait, which is a common rumor, but some conditions which premature babies have later in life, such as diabetes, are inherent. Age is also a factor which has no effect on bearing a premature child. Although older women tend to be less fertile and have a greater chance of bearing a baby with genetic defects, such as having Down’s Syndrome, they do not have to worry any more about having a baby born pre-term than a twenty or twenty-five year old woman. Although this is true, a mother who delivers one preterm baby is more likely to deliver another during her next pregnancy than a mother who hasn’t had a problem with previous pregnancy. Another high risk for premature pregnancy is when twins, or other multiple babies, are born. This occurs often because the mother’s body cannot hold more than one child for the normal full-term of thirty eight to forty two weeks, and must get rid of the children from the uterus in order to return the body to normal and prevent any injuries from occurring inside the mother’s womb.
Many advances are occurring everyday which enable mothers to feel safer with the care of premature babies. New drugs are being developed and new methods are being tested to ensure the security of a preemie, enabling the rate of deaths and the rate of premature babies born to both be lowered. As recently as 1986, premature babies had a much lower chance of survival, and with the help of experts, this factor has been greatly reduced. Hopefully, by the time our generation or our children’s generation begins to think about bearing children, there will not be much of a risk of having a premature baby.
Works Cited
Freeman, Roger, and Pescar, Susan. “Safe Delivery: Protecting Your Baby During High- Risk Pregnancy. New York: Facts on File, Inc., 1982. Golant, Susan and Ludington, Susan. Kangaroo Care The Best You Can Do To Help Your Preterm Infant. New York: Bantam Books, 1993. Griesemer, Bernard and Pfister, Fred. The Littlest Baby. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice- Hall Inc., 1983.
