Plant-like protest (phytoplankton)… contains flagella, are sensitive to light (eyespots), are autotrophic, and responsible for most of the oxygen in the air. Euglenophyta aka Euglena (plant like)
- No shells
- Can be photosynthetic but if in darkness long, will become saprophyte
- Found in stagnant and fresh water
- Asexual reproduction via binary fission
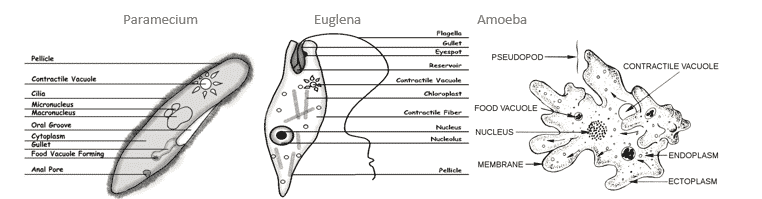
- Pellicle
Chrysophyta (diatoms and golden brown algae): Found in saltwater and fresh water
- Symmetrical, intricate silica valves and shells
- Used in toothpaste and polishes as fine abrasives (silica diatoms)
- Note: cell walls are made of pectin not cellulose
Pyrophyta (dinoflagellates): Found in ocean
- Golden algae and brown algae (dinoflagellates cause red tide – paralytic shellfish poisoning)
- Whale food
- Added to ice-cream and cream cheese to make smooth.
Animal-like protests (Zooplankton) found in water and moist environments, all heterotrophic
Sarcodina (amoeba, foraminifera’s and radio larins) intestines as parasites
- Moves and surrounds food with pseudopods
- Asexual reproduction
- Amoeba are the aquatic group (amoebic dysentery from poor sanitation and poor water treatment causes severe loss of fluids and blood, may lead to death)
Zoomastigophora (zooflagellates) found in both salt and fresh water, exists inside other organisms
- Have flagella
- Asexual reproduction
- Most are parasitic and cause diseases in other animals. Only exception is trichonympha (breaks down cellulose in the gut of termites providing energy). g. African sleeping sickness, tripanosoma carried by tsetse fly affects 5 million people per year = fever and chills, damages nervous system)
Ciliophora (most complex of all unicellular organisms): Found in water and soil (extremes of heat and cold)
- Typically asexual however can perform sexual reproduction through conjugation
- Moves by use of cilia which can cover the entire surface of the cell
- Paramecium
Sporozoa: live on/in their host
- All are parasitic, most are disease causing
- Asexual reproduction
- Lack cilia and flagella
- Depend entirely on host’s fluids for movement, move like a worm
- Animal-like protists harm other organisms by making plasmodium and sporozoan – they benefit other organisms by being linked to many food chains and digest cellulose
- Toxoplasmosis – from cat feces (can come from poorly cooked meat) to humans: crosses placenta and can cause miscarriage of unborn fetus
- Plasmodium – malaria – human to mosquito to human:
- Virax affects 200 million per year.
- Plasmodiurn carried by animal and vector hosts. Causes severe fever and chills, feel sleepy. Hosts are humans, mammals and primates. Occurs in tropical countries
Slime molds (fungus-like) (acrosiomycota and myxomycota)
- Similar to kingdom Protista because they can become amoeba like or have a flagella at some point in their life cycle
- Similar to fungi because they absorb nutrients through osmosis
- No real form (ooze)
- Produce spores during some point in their life cycle
Gymnomycota (name derived from the slime they leave behind when they move): found in cold shady moist places, under leaves, logs
Definitions:
- Endoplasm – fluid that fills the cell
- Macronucleus – large nucleus in ciliates
- Micronucleus – small that forms when chromosome is not incorporated
- Gullet – mouth of the cell where food enters
- Anal pore – Undigested materials move here and when contracts disposes of it
- Tricocysts – rod-like structure that is stuck out like a harpoon
- Cilia – hair-like structures used by microorganisms for movement
- Food vacuole – where food is stored inside a cell
- Contractile vacuole – eliminates excess water
- Oral groove – cell mouth before the gullet in a paramecium
- Flagellum – long tail-like structure for movement
- Eye spot – structure that detects light (for euglena to find the light for photosynthesis)
- Chloroplasts – where photosynthesis occurs
- Pellicle – thin layer supporting cell membrane that makes the cell flexible – many protozoa
- Nucleus – control centre of the cell
- Conjugation – two paramecium attach, in each cell 3 macronuclei disintegrate but 2 undergo miosis – significant because produce new combinations that provide additional survival chances
Relationships
- Euglena (euglenaphyta) and diatom (crysophyta): both are photosynthetic, plantlike protists with two cell walls
- Dinoflagellate (pyrrophyta) and bloom (population explosion of unicellular organisms – blooms are caused by dinoflagellates – blooms of certain dinoflagellates cause red tide)
- Slime mold (acrosiomycota or myxomycota)- makes bodies similar to a fungus and plasmodium (formed by slime mold)
- Phytoplankton and oxygen – phytoplankton produces most of Earth’s oxygen