> synapse: spaces between neurons, or between neurons and effectors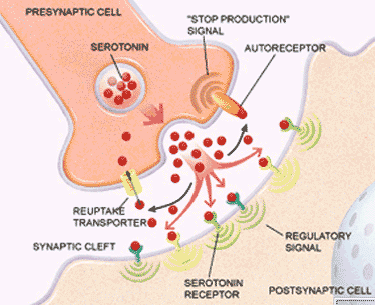
> vesicles containing chemical neurotransmitters are located at the end of neuron axons
Electrical Signals:
> electrical impulses moving along the axon stimulate the release of neurotransmitters
Chemical Signals:
> neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron and diffuse across the synaptic cleft
> neurotransmitters reaching the postsynaptic neuron depolarize it’s dendrites
Acetyolcholine and Cholinesterase:
Acetylcholine
> is an excitatory neurotransmitter -> causes depolarization on the postsynaptic neuron by opening Na+ ion channels
Cholinesterase
> destroys acetylcholine free floating and bound to receptors in a synapse
> causes Na+ ion channels to close and repolarization to occur -> neuron can be depolarized again
> not all neurotransmitters may be excitatory, some may be inhibitory -> preventing depolarization
> inhibitory neurotransmitters open more K+ gates, making the inside of the neuron even more negative; hyperpolarized
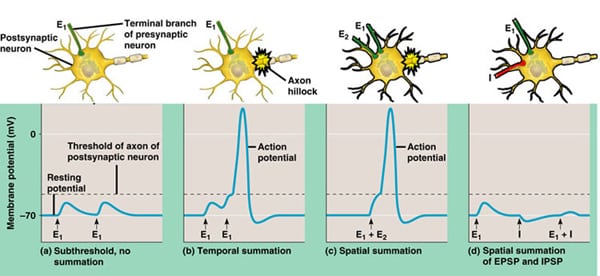
Summation
> the effect produced by the accumulation of neurotransmitters from two or more neurons
Excitatory and Inhibitory Neurotransmitters:
> both are used by your body to coordinate complex bodily functions
Example: throwing a ball
> excitatory neurotransmitters contract your triceps and inhibitory neurotransmitters relax your bicep, this prevents both muscles from pull against each another
Example: listening to a biology lecture
> excitatory neurotransmitters focus the lecture skills (listening, writing, eye movement, etc)
> inhibitory neurotransmitters suppress non essential information (temperature, pressure from clothes, etc)
> both types of neurotransmitters allow your CNS to prioritize information

Can you please describe the role of serotonin transporters (SERT)?
Its about time smoonee wrote about this.