The Inheritance of Difference: Eukaryotes & Prokaryotes
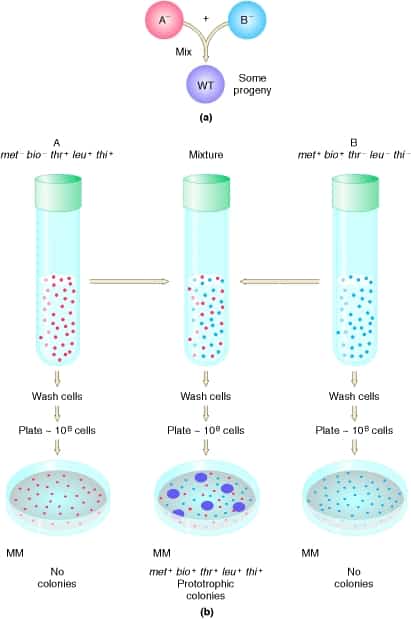
Inheritance of Different in Prokaryotes Mutations arise, move from donors to recipients, incorporated to recipients through recombination Transposition: some genes are mobile and can be transferred to another site, and then another host Transformation: the conversion of the heredity type of a cell by the uptake of DNA released by the breakdown of another cell…