Cells must perform thousands of different chemical reactions in order to survive. These reactions are crucial to providing cells with energy.
Endergonic reactions:
-“energy in” require energy in order to proceed
– biological endergonic reactions produce molecules that store energy (ex. Glucose)
– Ex. Photosynthesis
Exergonic reatctions:
– biological exergonic reactions release useable energy from glucose to form ATP molecules
– Ex. Cellular respiration
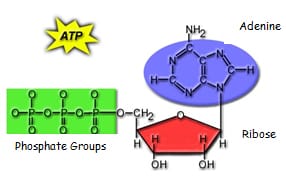
ATP is the energy molecule of cells
Importance of ATP:
– cells are efficient in their energy use; ATP provides this efficiency
– ATP is a small molecule that releases small enough quantities to be useful to the cell
– When a cell needs energy, it can use an appropriate number of small ATP molecules instead of wasting energy by spending a larger energy molecule (large carbohydrates)
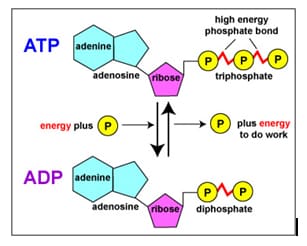
Storage and Release of Energy in a molecule of ATP:
Release of energy – the bond between the 2nd and 3rd phosphate group is broken, energy
a phosphate are released (about 30 kJ) producing ADP
Storage of energy – ADP can be converted back to a molecule of ATP, a bond forms between the 2nd phosphate group and a new 3rd phosphate when energy is supplied