Solute: substances that are dissolved in fluid (eg. salt)
Solvent: the liquid the solute is dissolved in (eg. water)
Passive Transport
movement of materials across a cell membrane without energy; Movement along a concentration gradient
Diffusion
- movement of particles from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration
- movement will continue until equilibrium is achieved
Example: – Perfume
– CO2 and O2 exchange in lungs
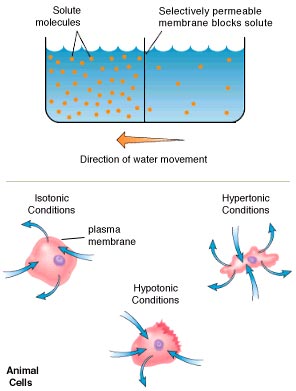
Osmosis
- diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane (eg. cell membrane)
- Water moves from higher concentration to lower concentration.
Hypertonic – the concentration of solutes outside the cell is higher than inside the cell.
- water moves out.
Isotonic – the concentration of solutes outside the cell is the same as inside the cell.
- equilibrium
Hypotonic – the concentration of solutes inside the cell is higher than outside the cell.
- water moves in.
- this is important to aquatic organisms
- Your kidney uses osmosis to regulate water balance in the blood. This determines the amount of water in urine.
Facilitated Diffusion
- Molecules too large for simple diffusion use protein carriers in the cell membrane to assist them. They pass through a protein, that acts like a channel in the membrane.
- Substances still move across a concentration gradient. No energy is used!!!!
Example
- Glucose is too large to diffuse through the membrane
- It uses the protein carriers to enter the cell – glucose is constantly being used up in a cell so there is a lower concentration inside the cell.
Active Transport – Using energy to move materials across the cell membrane; materials usually move against the concentration gradient
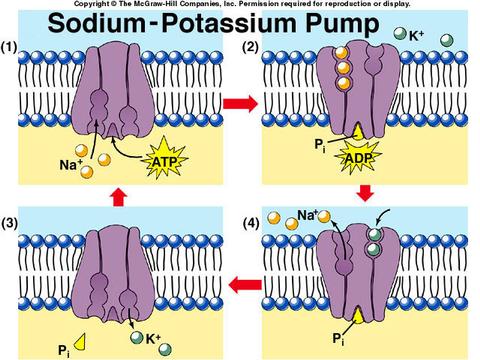
Sodium/Potassium Pump
- Located in nerve cells and critical to their function
- Nerve cells must maintain a higher concentration of Na+ outside the cell and K+ inside the cell.
- Special transport proteins in the membrane pump Na+ out of the cell and K+ into the cell. This takes energy
Endocytosis
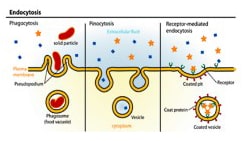
- moving materials into the cell by pinching the cell membrane
- this forms a vesicle inside the cell
- molecules too large to pass through the cell membrane
Phagocytosis “cell eating”– movement of large molecules
Example: how white blood cells “eat” bacteria
Pinocytosis “cell drinking” – transport of liquids into the cell
Exocytosis
- Exporting large molecules outside the cell
- A vesicle inside the cell fuses with the cell membrane and then releases it’s contents outside the cell.
Example: – how insulin is moved out of the pancreas into the blood