– the study of categorizing organisms
Binomial Nomenclature – two-part scientific naming of organisms
– the first word identifies the genus and the second word is the species
Example: Ursus americanus –
Ursus horribilis –
Ursus arctos –
Ursus maritimus –
NOTE: the format: capitals and italics
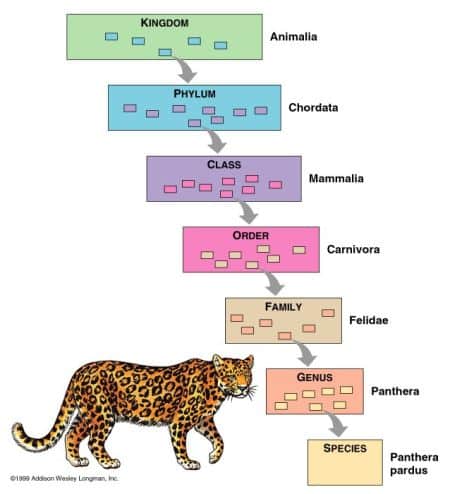
Levels of Classification (7) or Taxa:
“King Philip Came Over From Germany Swimming”
Example: HUMAN Dandelion
| Kingdom | Animalia | Plantae |
| Phylum | Chordate | Tracheophyta |
| Class | Mammalia | Angiospermae |
| Order | Primates | Asterates |
| Family | Homoinidae | Compositae |
| Genus | H*mo | Taraxacum |
| Species | sapiens | officinale |
KINGDOMS (6)
- Eubacteria – cell without a nucleus with rigid cell wall (peptidoglycan)
- Archabacteria – cell without a nucleus living in harsh conditions
- Protista – cell with a nucleus
- Fungi – multi-cellular heterotrophs with a cell wall
- Plantae – multi-cellular autotrophs
- Animalia – multi-cellular hetertrophs without a cell wall
Prokaryotic cells – do not have a nucleus
Eukaryotic cells – have a membrane bound nucleus
Phylogeny – history of evolution of organisms (phylogenetic tree)
Dichotomous Key – a two part key used to identify living things