Functions:
1. transport oxygen and carbon dioxide
2. distribute nutrients and transport of wastes
3. maintenance of body temperatures
4. circulation of hormones
Structure:
Made up of three components:
1. A fluid in which materials are transported (blood)
2. vessels in which the fluid moves (blood vessels)
3. a pump (the heart)
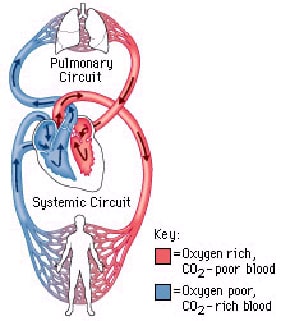
Circulatory system is actually two systems:
Pulmonary circuit:
-the right side of the heart pumps blood to the lungs
– blood picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide
– blood returns to the heart, on the left side
Systemic circuit:
– the left side of the heart pumps blood to all parts of the body
– blood delivers oxygen and other nutrients
– blood returns to the heart, on the right side
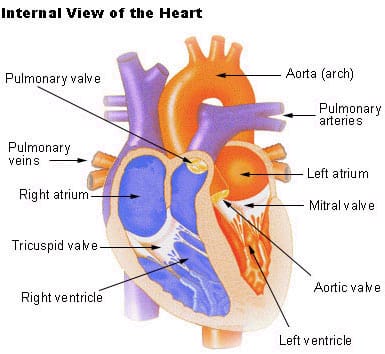
The Heart
– two pumps, each pump is separated by the septum; a muscle wall
– the right pump, pumps to the pulmonary circuit
– the left pump, pumps to the systemic circuit
-each pump is made up of an atrium and a ventricle
– atria receive blood from veins and pump into ventricles
– ventricles receive blood from atria and pump blood into arteries
– heart valves prevent blood from flowing backwards in the heart
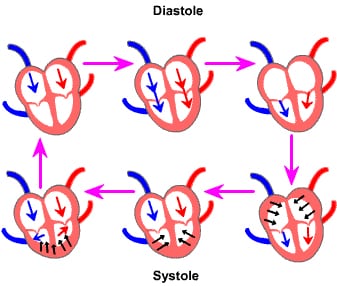
Heart Rhythms, Sounds and Pressure
– the sinoatrial node sets the heart rhythm, about 72 beats per minute
– the lubb-dubb heart sounds are caused by the closing of the valves
– diastole is when the heart is relaxed, fills up with blood (semilunar valves close)
– systole is when atria push blood into the ventricles, then the ventricles push blood into the arteries (AV valves close)