On a clear sunny day, the sky above us looks bright blue. Why is the sky blue? To answer these questions, we must learn about light, and the Earth’s atmosphere.
THE ATMOSPHERE
The atmosphere is the mixture of gas molecules and other materials surrounding the earth. It is made mostly of the gases nitrogen (78%), and oxygen (21%). Argon gas and water (in the form of vapor, droplets and ice crystals) are the next most common things. There are also small amounts of other gases, plus many small solid particles, like dust, soot and ashes, pollen, and salt from the oceans.
The composition of the atmosphere varies, depending on your location, the weather, and many other things. There may be more water in the air after a rainstorm, or near the ocean. Volcanoes can put large amounts of dust particles high into the atmosphere. Pollution can add different gases or dust and soot.
The atmosphere is densest (thickest) at the bottom, near the Earth. It gradually thins out as you go higher and higher up. There is no sharp break between the atmosphere and space.
LIGHT WAVES
Light is a kind of energy that radiates, or travels, in waves. Many different kinds of energy travel in waves. 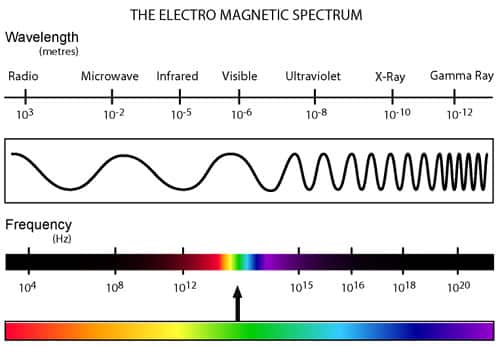 For example, sound is a wave of vibrating air. Light is a wave of vibrating electric and magnetic fields. It is one small part of a larger range of vibrating electromagnetic fields. This range is called the electromagnetic spectrum.
For example, sound is a wave of vibrating air. Light is a wave of vibrating electric and magnetic fields. It is one small part of a larger range of vibrating electromagnetic fields. This range is called the electromagnetic spectrum.
Electromagnetic waves travel through space at 299,792 km/sec (186,282 miles/sec). This is called the speed of light. The energy of the radiation depends on its wavelength and frequency. Wavelength is the distance between the tops (crests) of the waves. Frequency is the number of waves that pass by each second. The longer the wavelength of the light, the lower the frequency, and the less energy it contains. The spectrum ranges from waves of long wavelength (low frequency) to those of short wavelength (high frequency); it comprises, in order of increasing frequency (or decreasing wavelength): very-low-frequency to ultrahigh-frequency radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays.
COLORS OF LIGHT
Visible light is the part of the electromagnetic spectrum that our eyes can see. Light from the sun or a light bulb may look white, but it is actually a combination of many colors. We can see the different colors of the spectrum by splitting the light with a prism. The spectrum is also visible when you see a rainbow in the sky. The colors blend continuously into one another. At one end of the spectrum are the reds and oranges. These gradually shade into yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet. The colors have different wavelengths, frequencies, and energies. Violet has the shortest wavelength in the visible spectrum. That means it has the highest frequency and energy. Red has the longest wavelength, and lowest frequency and energy.
LIGHT IN THE AIR
Light travels through space in a straight line as long as nothing disturbs it. As light moves through the atmosphere, it continues to go straight until it bumps into a bit of dust or a gas molecule. Then what happens to the light depends on its wave length and the size of the thing it hits.
Dust particles and water droplets are much larger than the wavelength of visible light. When light hits these large particles, it gets reflected, or bounced off, in different directions. The different colors of light are all reflected by the particle in the same way. The reflected light appears white because it still contains all of the same colors.
Gas molecules are smaller than the wavelength of visible light. If light bumps into them, it acts differently. When light hits a gas molecule, some  of it may get absorbed. After a while, the molecule radiates (releases, or gives off) the light in a different direction. The color that is radiated is the same color that was absorbed. The different colors of light are affected differently. All of the colors can be absorbed. But the higher frequencies (blues) are absorbed more often than the lower frequencies (reds). This process is called Rayleigh scattering. (It is named after Lord John Rayleigh, an English physicist, who first described it in the 1870’s.)
of it may get absorbed. After a while, the molecule radiates (releases, or gives off) the light in a different direction. The color that is radiated is the same color that was absorbed. The different colors of light are affected differently. All of the colors can be absorbed. But the higher frequencies (blues) are absorbed more often than the lower frequencies (reds). This process is called Rayleigh scattering. (It is named after Lord John Rayleigh, an English physicist, who first described it in the 1870’s.)
WHY IS THE SKY BLUE?
The blue colour of the sky is due to Rayleigh scattering. As light moves through the atmosphere, most of the longer wavelengths pass straight through. Little of the red, orange and yellow light is affected by the air. However, much of the shorter wavelength light is absorbed by the gas molecules. The absorbed blue light is then radiated in different directions. It gets scattered all around the sky. Whichever direction you look, some of this scattered blue light reaches you. Since you see the blue light from everywhere overhead, the sky looks blue.
As you look closer to the horizon, the sky appears much paler in color. To reach you, the scattered blue light must pass through more air. Some of it gets scattered away again in other directions. Less blue light reaches your eyes. The color of the sky near the horizon appears paler or white.The sky is filled with air. Air is a mixture of tiny gas molecules and small bits of solid stuff, like dust.
As sunlight goes through the air, it bumps into the molecules and dust. When light hits a gas molecule, it may bounce off in a different direction. Some colors of light, like red and orange, pass straight through the air. But most of the blue light bounces off in all directions. In this way, the blue light gets scattered all around the sky.
When you look up, some of this blue light reaches your eyes from all over the sky. Since you see blue light from everywhere overhead, the sky looks blue.
THE BLACK SKY AND WHITE SUN
On Earth, the sun appears yellow. If you were out in space, or on the moon, the sun would look white. In space, there is no atmosphere to scatter  the sun’s light. On Earth, some of the shorter wavelength light (the blues and violets) are removed from the direct rays of the sun by scattering. The remaining colors together appear yellow. Also, out in space, the sky looks dark and black, instead of blue. This is because there is no atmosphere. There is no scattered light to reach your eyes. Light is a kind of energy that can travel through space. Light from the sun or a light bulb looks white, but it is really a mixture of many colours. The colours in white light are red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet. You can see these colors when you look at a rainbow in the sky. In space, there is no air. Because there is nothing for the light to bounce off, it just goes straight. None of the light gets scattered, and the “sky” looks dark and black.
the sun’s light. On Earth, some of the shorter wavelength light (the blues and violets) are removed from the direct rays of the sun by scattering. The remaining colors together appear yellow. Also, out in space, the sky looks dark and black, instead of blue. This is because there is no atmosphere. There is no scattered light to reach your eyes. Light is a kind of energy that can travel through space. Light from the sun or a light bulb looks white, but it is really a mixture of many colours. The colours in white light are red, orange, yellow, green, blue and violet. You can see these colors when you look at a rainbow in the sky. In space, there is no air. Because there is nothing for the light to bounce off, it just goes straight. None of the light gets scattered, and the “sky” looks dark and black.
The sky is blue during the day but black on the moon, the colour of the sky is affected by the wavelength of the colour, light scattering and the atmosphere. The earth atmosphere is primarily made of oxygen and nitrogen; both of these gases are made up of same size of particles of atoms. The sun produces light in the form of ultraviolet rays, which pass through the electromagnetic spectrum that consists of mixture of colours with different wavelengths.
When the rays from the sun pass through the spectrum the colour with the shorter wavelength is scattered within the atmosphere. The blue and violent light waves both have shorter wavelengths because of that they are scattered by the rays, but we mainly see blue. Waves with short wavelength have the highest frequency. When the waves of blue light pass through the earth‘s atmosphere many of the particles eventually crash into the relatively large atoms of oxygen and nitrogen. They bounce off scattered and then they go all direction around the atmosphere that’s what makes the sky to be blue in colour, there are electromagnetic waves traveling through space.
If you were out in the space or on the moon the sun would look white. In space there is no atmosphere to scatter the light. On earth some of the shorter wavelength light waves are removed from the direct rays of the sun by scattering. In space, there is no air. Because there is nothing for the light to bounce off, it just goes straight. None of the light gets scattered, and the “sky” looks dark and black.
