Dihybrid cross = involves inheritance of 2 characteristics
Example 1:
In Pisum sativum, a round seed is produced by a dominant allele (R), while wrinkled seeds are produced by the recessive allele (r). Yellow seeds are produced by the dominant allele (Y), while green seeds are produced by the recessive allele (y).
In a cross between a homozygous round, yellow plant and a wrinkled green plant, what is the F1 and F2 phenotypic and genotypic ratio?
Key: R = round seed Y = yellow seeds
r = wrinkled seed y = green seeds
P1: round yellow seed x wrinkled green seed
RRYY rryy
Gametes: R, Y r, y
| ry | ry | |
| RY | RrYy | RrYy |
| RY | RrYy | RrYy |
F1: Genotypic Ratio: 100% heterozygous RrYy
Phenotypic Ratio: 100% round, yellow seeds
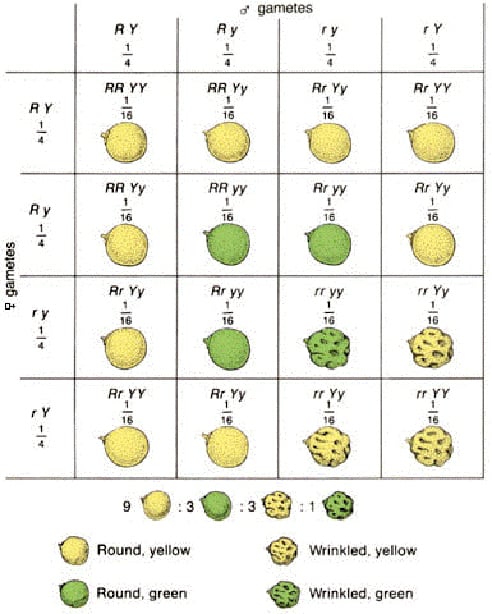
F2: Crossing F1 plants among themselves produces an F2 generation.
P2: round yellow seed x round yellow seeds:
RrYy RrYy
Possible Gametes:
RY, Ry, rY, ry RY, Ry, rY, ry