Mutations are errors made in the DNA sequence than can have negative side effects, no effect, or positive effects for an organism
Point Mutations
Mutations that occur at a certain point in the DNA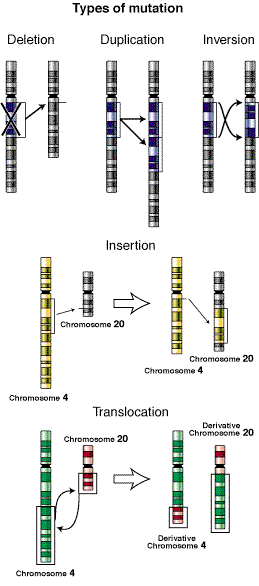
Substitution – the replacement of one base in a DNA sequence by another base
Deletion – the elimination of a base pair or group of base pairs from a DNA sequence
Insertion – the placement of an extra nucleotide in a DNA sequence
Substitution Errors:
Silent mutations:
– a mutation that does not result in a change in the amino acid coded for and, therefore, has no effect on the operation of the organism
– could be an error in an intron or in the 3rd base pair of a codon
Missense mutations:
– a change that leads to a different amino acid being placed in the protein sequence
– will cause a change in protein conformation (shape) à may be bad or may have no affect
Nonsense mutations:
– a change that causes a stop codon to replace a codon for an amino acid
– translation stops prematurely -> produces nonfunctional proteins ->often lethal
Insertion/Deletion Errors:
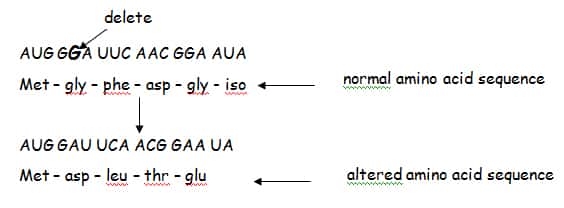
Frameshift mutations:
– caused by the insertion or deletion of one or two nucleotides in the DNA sequence
– drastic errors; can result in many different amino acids substituted or a stop codon read normal amino acid sequence:
Chromosomal Errors
A translocation is the transfer and exchange of a fragment of DNA between two nonhomologous chromosomes
– if they happen to fall within a coding region of a gene, they will disrupt the correct transcription of the gene
An inversion is a chromosomal segment that has reversed it’s orientation in the chromosome causing the gene to be disrupted
Causes of Genetic Mutations
Spontaneous mutations – mutations caused by errors in DNA replication or crossing over in meiosis
Induced mutations – mutations caused by mutagenic agents like UV radiation, cosmic rays, X rays, and certain chemicals