Atoms
An atom is a building block of all matter (all things that are solid/liquid/gas). An atom the smallest single building block that makes up all mater. An atom is made of: protons, neutrons and electrons.
Element
An element is 2 or more of the same atom.
E.g. – O3.
The periodic table of elements is a list of 118 elements known to science.
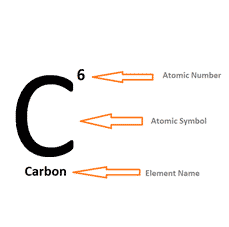
Atomic No: The number of protons in the nucleus.
The first letter is always uppercase. The second/third letter is always lowercase.
An atom is a single. An element is made of multiple atoms that are the same. A compound is made of multiple atoms that are different.
Compound
A compound is a special molecule that has 2 or more different atoms in a ratio.
E.g. – HNO3, CO2.
Molecule
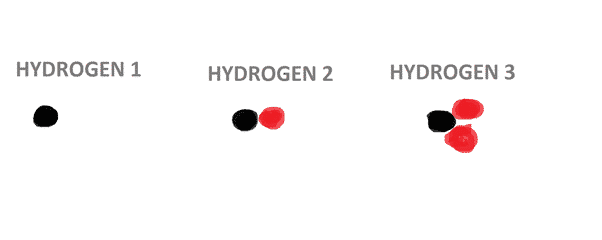
2 or more atoms in a special ratio.
E.g. – H2O.
Ion
An ion is a charged atom that has lost or gained an electron. Cation = lost electron. Anion = gained electron.
A cation is a positive ion it has LOST electrons.
Na+ – Sodium ion has lost 1 electron. Cation is a positive ion.
Mg2+ – Magnesium ion lost 2 electrons. 12+ 10-.
Li+ – Lithium ion 1 electron. 3+ 2-.
Ca2+ – Calcium lost 2 electron. 20+ 18-.
An anion is a negative ion it has GAINED electrons.
Cl– – Chlorine has gained 1 electrons. 17+ 18-.
Br– – Bromine has gained 1 electrons. 35+ 36-.
O2– – Oxygen has gained 2 electrons. 8+ 10-.
Isotope
An isotope is an atom that has the same of the number of protons but different number of neutrons.
Atomic No: the number of PROTONS in the nucleus of an atom.
Mass No: the number of PROTONS + NEUTRONS in the nucleus of an atom.
LENSES
A lens is a transparent piece of plastic or glass that is shaped to curve inwards or outwards. A lens refracts light.
There are two types of lenses: Convex and Concave
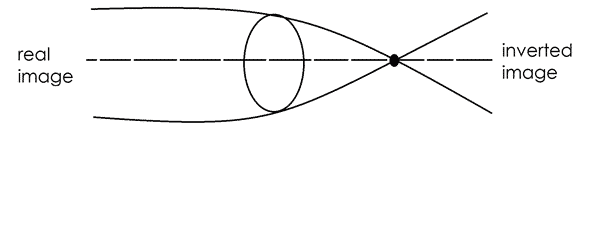
CONVEX LENS
A convex lens bends light in, converges light to a point called the focal point. A convex lens is also called a converging lens.
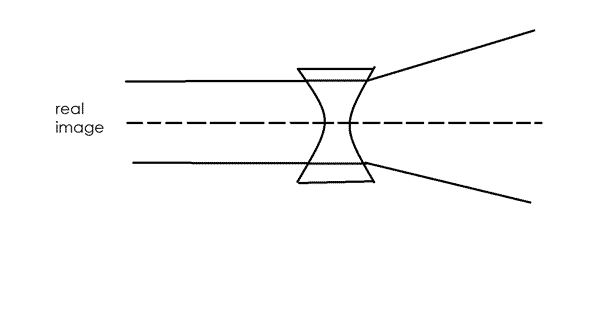
CONCAVE LENS
A diverging lens spreads light out, diverges light out.
(light dies in a cave concave = diverging)
Light
Light is a form of energy called electromagnetic radiation. Light travels as waves, e.g. UV rays, X-rays, infrared light, and microwaves. Light is the fastest thing in the universe. Light travels at a speed of 300,000 km per seconds.
- Transparent: allowing light to pass through so that objects behind can be distinctly seen
- Translucent: allowing light to pass through but not detailed shapes, to pass through
- Opaque: not allowing light to pass through
RADIATION
Radiation transmits heat as invisible waves that travels at the speed of light (around 300,000 km per second).
Forms of radiation:
- Light
- Infrared – night vision
- Heat is radiated from fires
- UV rays
- Radiation for cancer kills cancer cells
Radiation can be:
- Absorbed – taken into the object especially black and dark colours
- Reflected – the heat energy bounces off as waves
- Transmitted – transmit means ‘travels through’. The waves pass through glass
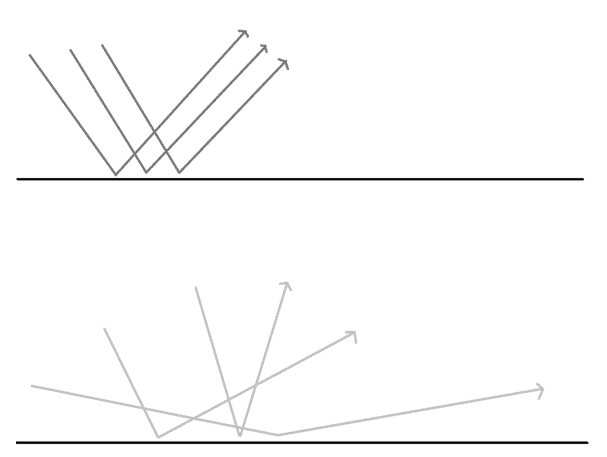
Reflection
Regular reflection is when an image is seen in a flat surface. The light rays are reflected back.
Diffuse reflection is when no image is seen in a rough surface because the light is reflected back at all angles.
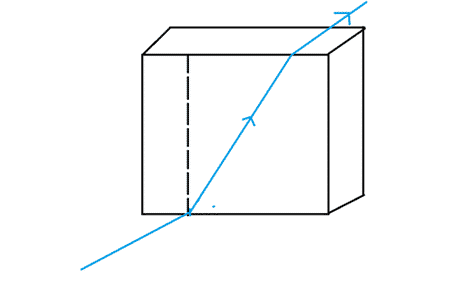
Refraction
Refraction is the bending of the light. Refraction occur when it passes from a medium with a different density.
Solubility
Solubility is how easily an ionic compound dissolves.
SOUND
What is sound?
Sound is produced when something vibrates. E.g. speech – flaps of skin vibrate, and drum – strings inside the piano vibrate.
Sound is produced when something vibrates so it makes particles in the air vibrate.
A sound wave is the movement of alternating compressions and rarefactions.
Sound waves rely on particles to vibrate in: sold, liquid and air.
Compression
Compression is when vibrations creates regions of space in which the air particles are bunched together.
Rarefaction
Rarefaction is when air particles are more spread out.
THERMAL EQUILIBRIUM
Radiation: is a form of heat transfer by invisible waves. Radiation does not transfer from particle to particle, instead it travels through vacuum.