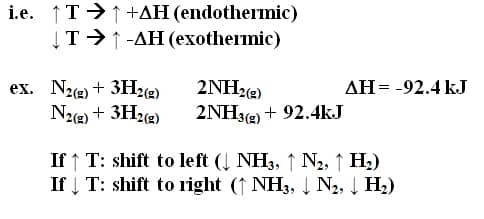
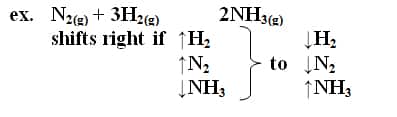If an equilibrium in a system is upset, the system will tend to react in a direction that will re-establish equilibrium
1) Adding or Removing a Reactant or Product
– reaction shifts in a direction that will remove a substance added or replace a substance removed
2) Changes of Temperature
– increasing temperature shifts a reaction in a direction that produces an endothermic change
3) Changing Volume in Gaseous Reactions
– decreasing volume of a gaseous reaction mixture causes reaction to decrease number of molecules of gas (if it can)
4) Effect of Catalyst
– lower activation energy for forward and reverse reactions by equal amount
=> affect both rates equally
– cause reactions to reach equilibrium more rapidly
5) Addition of an Inert Gas at Constant Volume
– inert gas will not react with any equilibrium participants
– no affect on equilibrium (no effect on [ ] of participants)
- no change in position of equilibrium