Defining Characteristics of the Plant Kingdom:
- Multicellular
- Terrestrial
- Embryophytes
- Photosynthetic (almost all)
- Eukaryotic
4 Major Groups
1. Non-Vascular Plants (Bryophytes and Friends)
- No vascular tissue – therefore must rely on surrounding moisture and osmosis to move fluids through their bodies.
- Small in stature, and simplistic – NO organs (roots, leaves, stems) (Rhizoids = root-like structures that provide minimal anchorage / absorption).
- Pioneer plants – lay the foundation for other plant growth, prevent erosion.
- Use spores to reproduce (sexual) – require water for sexual fertilization. Also capable of fragmentation (asexual).
- Alternation of Generations – lush “mat”-like body = haploid gametophyte generation (produces gametes through mitosis), stalk-like sporophyte generation (diploid) forms when gametes unite and produces haploid spores (that grow into individual male / female gametophytes that produce gametes through mitosis, etc.) through meiosis.
- Examples = Mosses, Liverworts, Hornworts, (3 non-vascular phyla), All groups below = Vascular plants = Tracheophytes
2. Vascular Seedless Plants (Pteridophytes and Friends)
- Have vascular tissue to transport fluids.
- Diverse form – 2mm to 15 m in height. True roots, stems, leaves.
- Like mosses = Pioneer plants.
- Alternation of Generations – familiar fern body (frond) = diploid sporophyte generation (underneath the fronds are brown sporangia that produce spores via meiosis). Heart shaped prothallus at base of frond = haploid gametophyte generation which produces gametes via mitosis.
- Use spores to reproduce (sexual) – require water for sexual fertilization. Also capable of fragmentation (asexual).
- Examples = Ferns, Horestails, Club Mosses, Whisk ferns (4 vascular, seedless phyla), All Groups Below = Seed Plants = Spermatophytes
3. Vascular Seed Plants (Naked) – Gymnosperms (Conifers and Friends)
- Have vascular tissue
- Cones = reproductive structures
- Pollen to transport sperm – no need for water
- Leaves typically = needles/scales
- Examples = Conifers (pines, firs, yew, junipers, cedars), Gingkos, Cycads, Ephedra (4 vascular seed phyla)
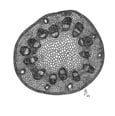
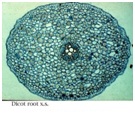
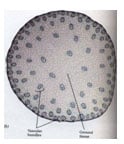
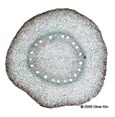
4. Vascular Seed Plants (Covered) – Angiosperms
- Have vascular tissue
- Flowers = reproductive structures
- Pollen to transport sperm – no need for water
- 2 major classes: Monocots and Dicots