Energy Content of Food Lab Report Answers
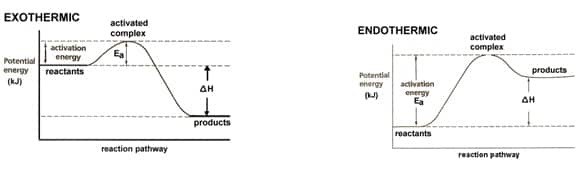
Research question: All organisms have activities, organisms use energy to accomplish activates. Organisms eat food to gain energy, this energy is stored for later use. Since humans are organisms we eat food to gain energy. Which food of the same category gives us more energy? Hypothesis: Since fat is the main reserve that is burnt…