Cellular Respiration: Glycolysis, Pyruvate, Krebs
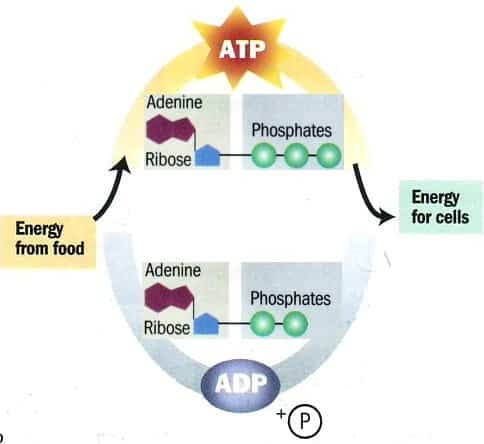
Chemical Basis of Cellular Respiration Allows for the extraction of energy from sugars (i.e glucose) by slowing oxidizing it This process converts potential chemical energy into ATP (which can be used by a majority of reactions) C-H bonds (those found in glucose) are the primary energy bond found in organic molecules (i.e glucose, octane etc.)…