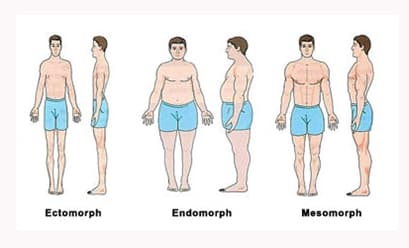
Body Types (Somatype)
Attempting to enter the basic American search for self-control, individuality and thinness has not brought most people more health and happiness. Instead, we often feel as if we have failed and the blame is laid squarely on our shoulders. But the social requirement that we achieve the “ideal weight” is based on the presumption that…