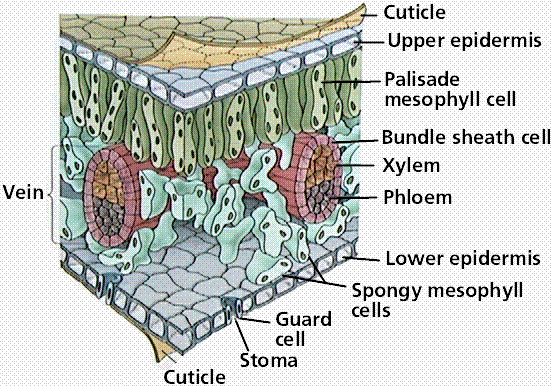
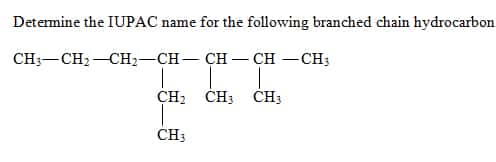
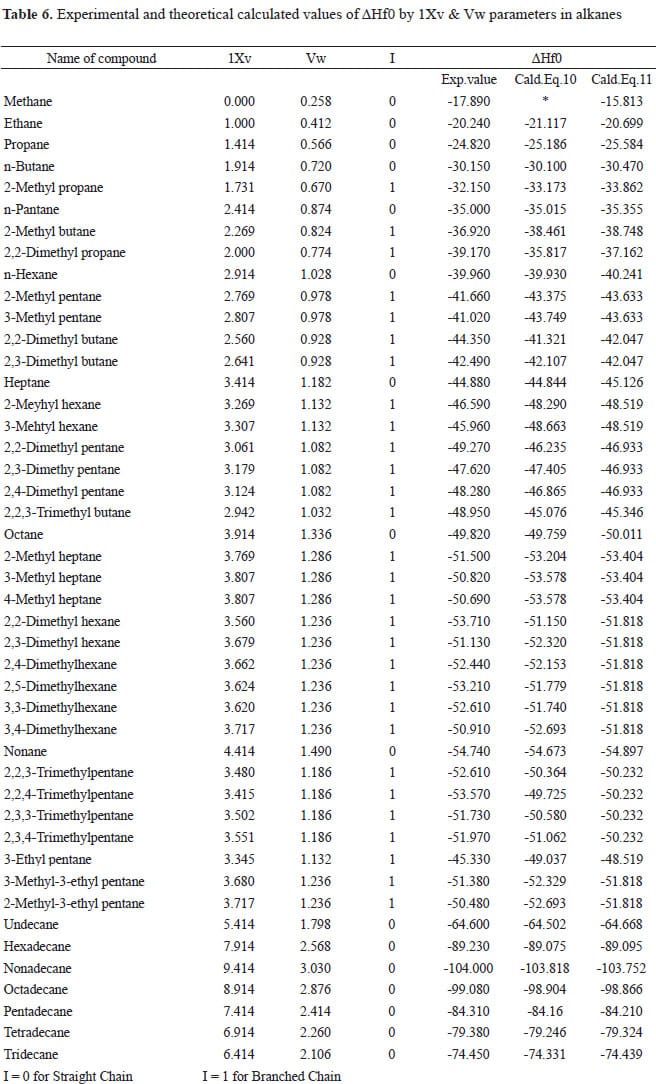
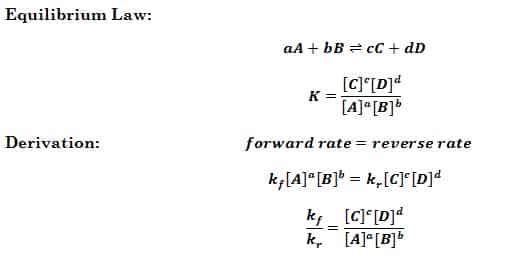The Equilibrium Constant (K)
Where K is the equilibrium constant, A,B,C,D are the equilibrium concentrations of aqueous/gaseous compounds, a,b,c,d are the coefficients in the balanced chemical equation. The equilibrium constant is related to the rate constants of the forward and reverse reactions. It is always the same for a given reaction at a given temperature. Since k changes with…