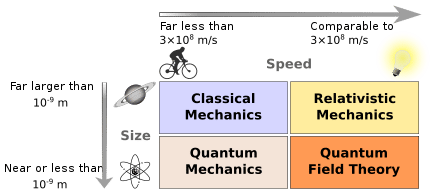
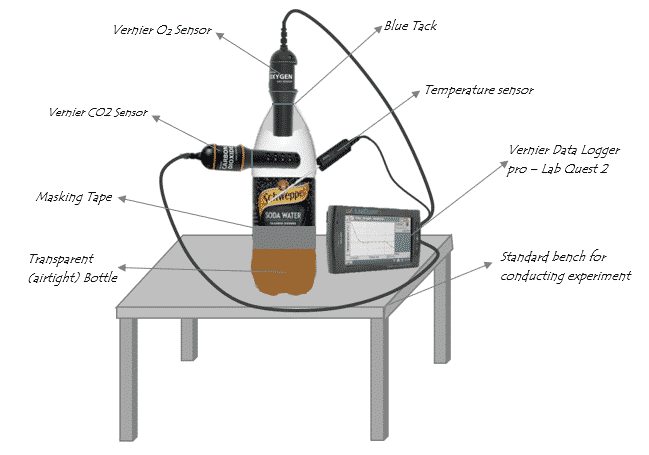
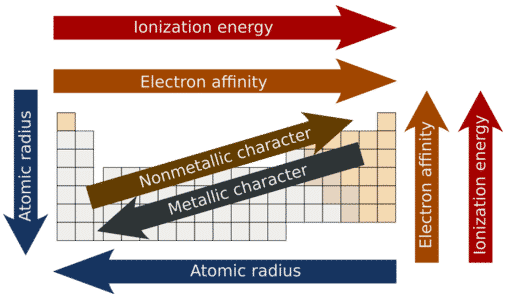
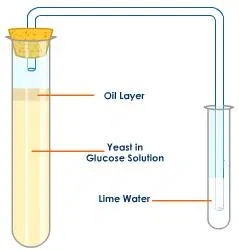
Earth Sciences Study Guide: Atmospheric Structure & Composition
Of what two gases was Earth’s first atmosphere primarily composed? diatomic nitrogen, carbon dioxide What are the percentages of Earth’s three most abundant constant (non-variable) gases in the atmosphere? nitrogen (78.08%), diatomic oxygen (20.95%), argon (0.93%) What are the variable gas within Earth’s atmosphere? water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, hydrogen, nitrous oxide,…