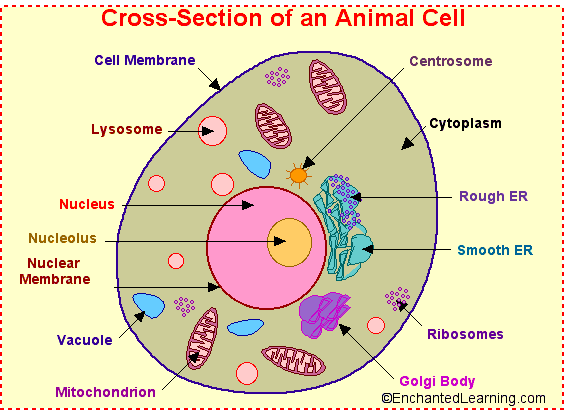
Lunar Maria: Facts & Topography
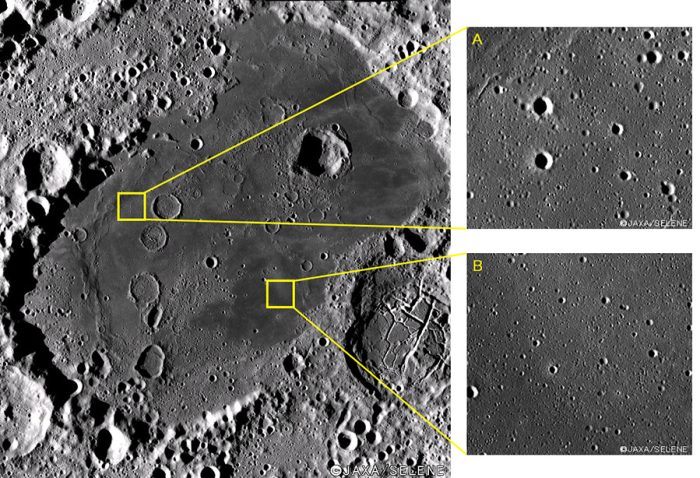
From Earth, one can look towards the night sky and observe that the moon appears to have areas that are lighter, and areas that are considerably darker. These dark areas are referred to as lunar maria, which are basically land basins on the moon in varying sizes. These basins were formed when hot, molten lava…