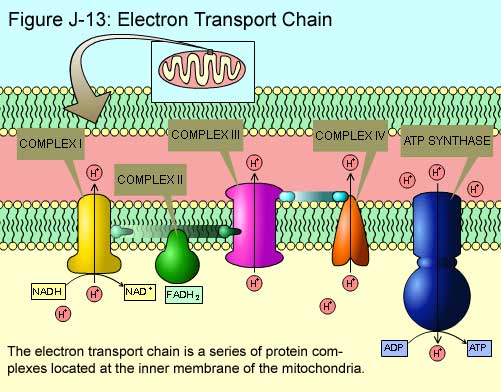
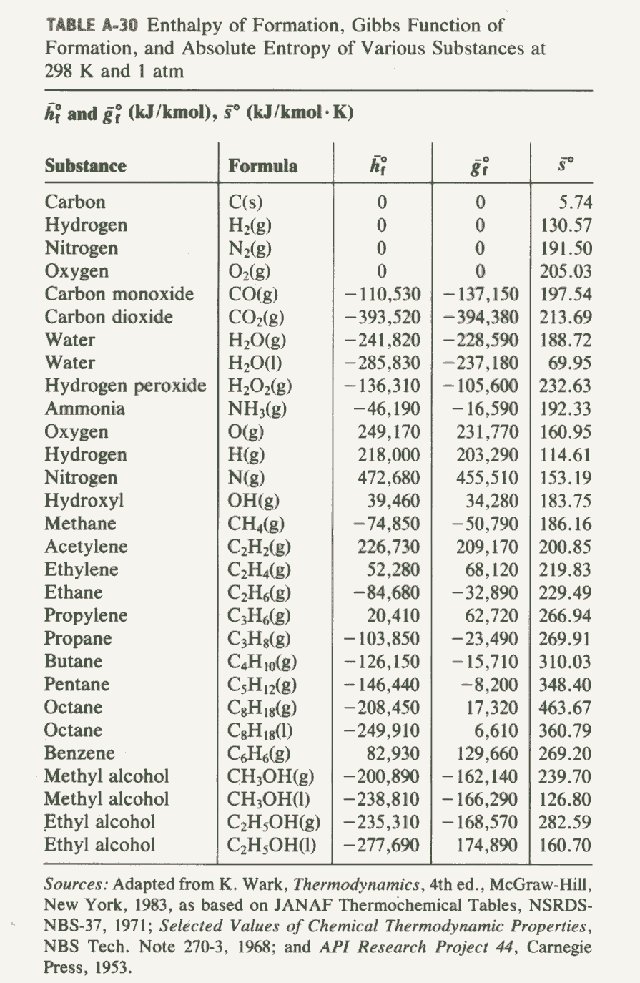
Electron Transport and Chemiosmosis
NADH and FADH2 carry electrons to the ETC Each become oxidized, losing two electrons to the ETC The Electron Transport Chain (ETC) Structure Located within the inner mitochondrial membrane Composed of various protein structures arranged in order of increasing electronegativity Ex. weakest electron attractor (NADH dehydrogenase) is at the beginning of the chain and the…