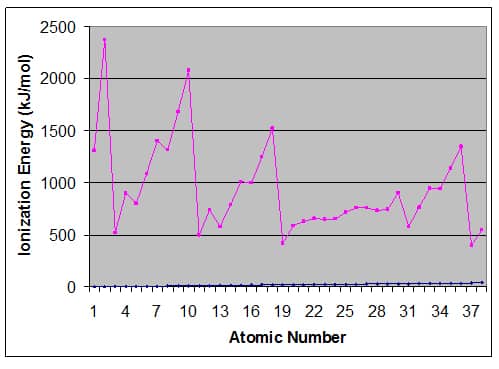
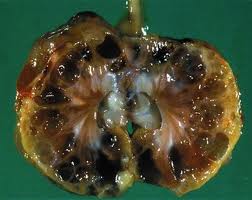
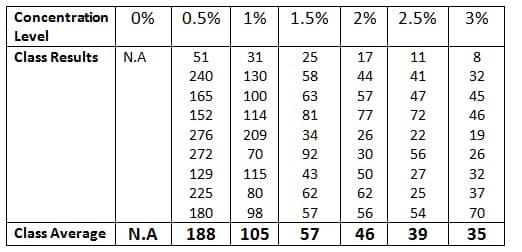
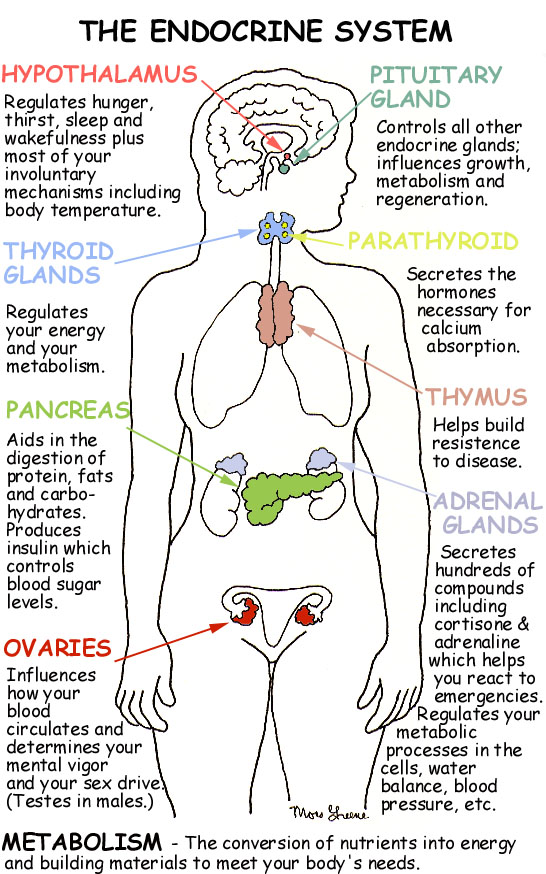
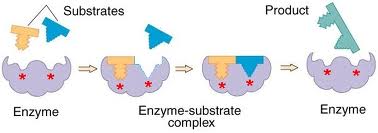
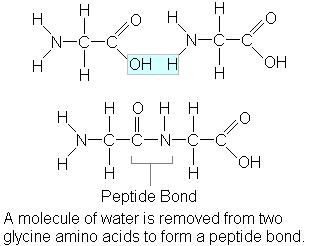
DDT: Environmental Impact, Dangers, History
Pests have plagued humanity for as long as history has been kept, leading to many diseases in the process. Many people have tried to fight these pests and diseases, but came up empty. DDT was the world’s first known pesticide and is arguably the world’s most well known. DDT was first synthesized by Othmar Ziedler…