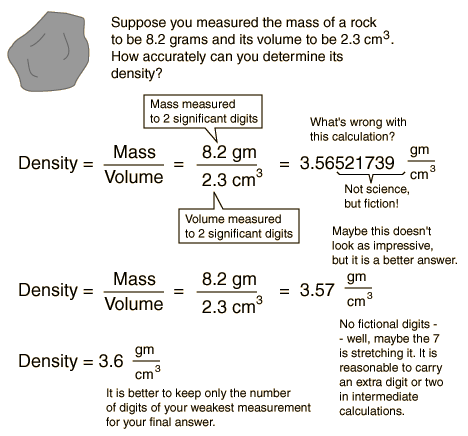
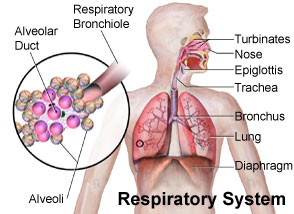
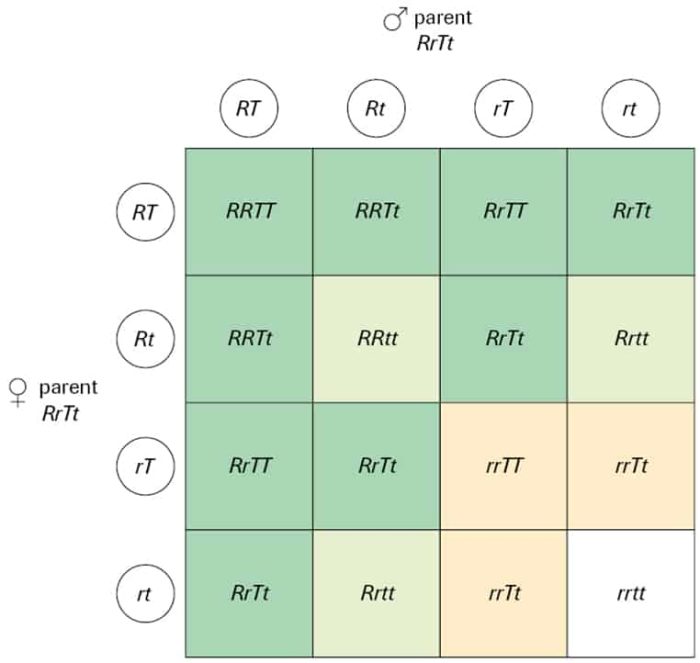
Significant Digits Rules
The number of significant digits in an answer to a calculation will depend on the number of significant digits in the given data, as discussed in the rules below. Approximate calculations (order-of-magnitude estimates) always result in answers with only one or two significant digits. When are Digits Significant? Non-zero digits are always significant. Thus, 22…