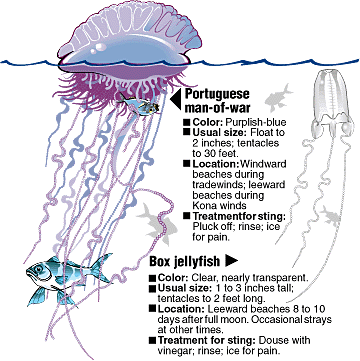
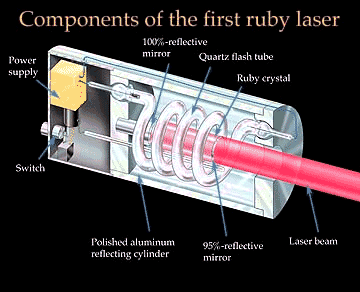
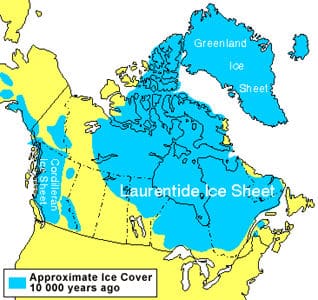
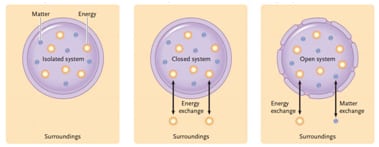
Darwinian Explanation: Cheetah Evolution
Today’s modern cheetahs can run 60 mph to catch prey. Their ancestors could originally only run 20 mph. There was selective pressure in the environment of cheetahs that demanded for faster cheetahs to catch more prey because there was a battle for survival. There was variation in the ancestral population. Some cheetahs could run faster…