William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
Charles Dicken’s ‘Oliver Twist’ shows how an individual’s opportunities in life can be both restricted and improved through their interactions to a large extent by showing us the different types of people that you could come across in Victorian London. The plot is about an orphan who sets out into London looking for a way…
Null hypothesis: is the claim being assessed in a hypothesis. For a claim to be a testable null hypothesis, it must specify a value for some population parameter that can form the basis for assuming a sampling distribution for a test statistic. Alternative hypothesis: The alternative hypothesis proposes what we should conclude if we find…
“We know what we are, but we know not what we may be.” -William Shakespeare. In the poem of Romeo and Juliet written by William Shakespeare, the main characters, Romeo and Juliet, described as “star-crossed lovers”, die tragically. In the plot, the Capulet and Montague families have had an ancient grudge against each other which…
The two poems written by William Blake feature animals that are antithetical, one symbolizing the goodness, peace, harmony and unity in the world whilst the other the presence of darkness in the world. Blake makes a similarity between a lamb and a child which are both gentle, mild, and crooning, giving us the sense of…
The poem is a monologue in which the poet talks to himself, the spirit of the nature and at times to his sister. Wordsworth’s ”Tintern Abbey” takes on an opulence of ideas regarding nature’s ability to conserve memory, and grasp the past and the present. Through his writing, Wordsworth conveys his experiences with nature to…
Historical Development of Databases Hierarchical Database Model A data model in which data is organized in a top-down, or inverted tree structure with lower level records subordinate to higher-level records A lower level record is called a child and a higher level record is called a parent Each parent record can have many child records,…
Many writers, artists, and poets have a very specific style that is unique to them and resonates throughout their work. Although there are many similarities between their works, there are apparent differences between each one. William Blake, a poet, wrote two books, first one being ‘Songs of Innocence’ and later on wrote another one named…
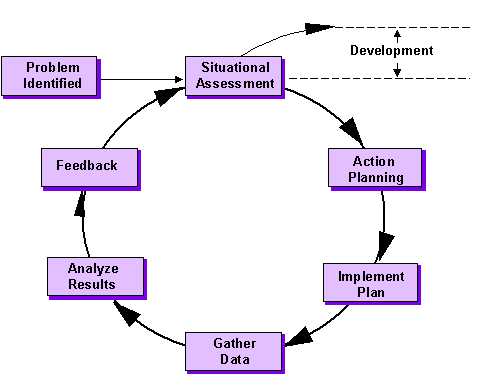
The OD cycle is a framework that is used to solve problems that have been identified in a firm. Since a problem might adversely affect a firm’s objectives, it becomes important for the management to get rid of it as soon as possible. The OD cycle outlines the steps the firm ought to follow to…
You’ve generally thought about how life would resemble being incredibly wealthy, it generally enters our thoughts when we find out about the lottery. The glorious dreams of a lavish way of life interest us as we scratch out that lottery card. In any case, what are the chances of winning? The insights are overpowering to…
Table 1. Solution concentrations, volumes and observations for Experiment 1: Observing the enzyme reaction. Test Tube dH20 Potato Extract Catechol Observations 1 5 ml + 500μl —– 500μL Solution turned milky-white to clear. (High substrate) 2 5 ml 500μl 500μl Solution turned yellowish-brown. (High substrate) 3 5 ml + 500μl 500μl —– Solution is clear,…
From Figure 4.2, describe the geographic locations where coastal upwelling is important (e.g., “west central and southwestern South America”). Upwelling causes some of the coldest surface temperatures on Earth. The low surface temperatures stabilize the overlying atmosphere, causing cool dry climates (deserts) to dominate the western edge of South America. Upwelling is important where coastlines…
Through which city does the prime meridian run? Greenwich, England What are the dates of the solstices and equinoxes? Summer solstice: June 21 Winter solstice: December 22 Vernal equinox: March 21 Autumnal equinox: September 22 Describe Earth–Sun relationships in terms of orbit, the Sun’s position, tilt and direction of Earth’s axis as it…
Of what two gases was Earth’s first atmosphere primarily composed? diatomic nitrogen, carbon dioxide What are the percentages of Earth’s three most abundant constant (non-variable) gases in the atmosphere? nitrogen (78.08%), diatomic oxygen (20.95%), argon (0.93%) What are the variable gas within Earth’s atmosphere? water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, hydrogen, nitrous oxide,…
The nature of unexpected discovery entails a journey that is transformative and concerns one’s relationship with one’s self or one’s world. Discoveries can be either sought or serendipitous and can lead to good or bad consequences, but ultimately they are all concerned with the acquisition of greater knowledge and a new perspective. In William Shakespeare’s…
As said by Tony Dungy, “The secret to success is good leadership, and good leadership is all about making the lives of your team members or workers better.” But what makes a great leader? Many other people would agree that for a leader to be a great one, they must be chosen based on key…
The intricate and tumultuous relationship between Britain and India has spanned the course of hundreds of years. Contact between Britain and India and been steadily increasing since the 17th century. While at first, both countries enjoyed varying levels of positive trade between them, Britain had soon expanded its growing empire to India and it became…
18.1 – 8a – globalization: characteristics and trends Globalization – the movement toward a more integrated and interdependent world economy People are buying more foreign products 16.1 – International Trade – absolute and comparative advantage Why nations trade Specialization is an important reason for trade Exports – the goods and services that a nation sells…
12.1 – measuring the nation’s output and income Macroeconomics – part of economics that deals with the economy as a whole and uses aggregate measures of output, income, prices, and employment Gross Domestic Product is one of the most important macro measures that keep track of nation’s production, consumption, saving, and investment. GDP – The…
Unit 6 – Money, Banking, and the Fed Chapter 14.1 – The evolution, functions, and characteristics of money Federal Reserve System (Fed) – private owned, publicly controlled central bank of the united states Federal reserve note – paper currency issued by the Fed in use today The evolution of money Barter economy – moneyless economy…
Section 9.1 – economic impact of taxes When a tax is placed, the good or service raises the cost of production and the price of the product With less products sold, resources has to be cut from a business Can be used to encourage/discourage certain types of activities Sin tax – relatively high tax designed…