Tutor and Freelance Writer. Science Teacher and Lover of Essays.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2024 | Creative Commons 4.0
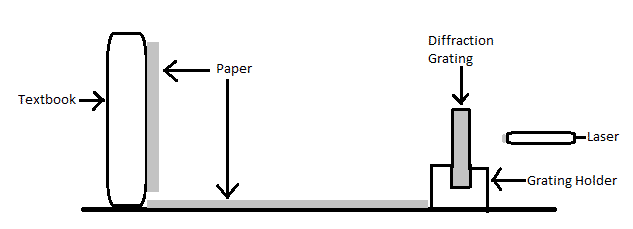
Abstract Using the formula λ = ∆x L / d, we will determine the wavelength of a red laser to be 641nm. Using this information we will then determine the track spacing for a CD and DVD. We calculate the track spacing for the CD to be 1.5 μm and the track spacing for the…
Community: A group of species that occupy a given area, interacting either directly or indirectly Predation Consumption of one organism by another organism Predator-prey population oscillations Predators and prey are agents of natural selection for each other defense or attack strategies camouflage aposematic colouration Mimicry Batesian: One species is harmful the other is non-harmful Non-harmful…
“In order to understand the whole world, one must first understand Mississippi” (). This thought was penned by William Faulkner, author of a Rose for Emily and several other stories set deep in the American South. Faulkner is considered to be one of the foremost Southern writers, and his work takes place almost exclusively in…
In the thirteenth century when Sir Gawain and the Green Knight was written, as well as in the Arthurian era in which it took place, Christian traditions created a male-dominated society in which women had very little perceived power. The paradigm of women in this era was a delicate paradox- they were treated with idolatry…
The pursuit of any success in life is an arduous journey, one that can only be accomplished by the few dedicated individuals willing to push their ambition and capabilities as far as possible. Only a minute handful of people make it to a professional sports level, a great actor or actress, or even a great…
In the 1930s, all the world was struggling to get by, trapped in the international financial stranglehold now known as the Depression. While most countries were plagued by economic difficulty, none was so affected as Germany. As the defeated party in world war one, the Germans were responsible for the brunt of a war reparations…
Crouteau and Hoynes addressed many of the characteristics of CNNization with depth and insight, but they did not adequately address one of the most important results of 24/7 media- myth and misinformation in the news. That is not to say that there were not errors in the media before CNN came into existence. However, the…
The Industrial Revolutions of the 18th and 19th centuries gave birth to several innovative thinkers and industrialists. With their countless contributions to the industrial process, these people made Western society economically, socially, and politically sound, as it is today. However, this progress conflicts enormously with the modern concepts of morality. The exploitation of workers and…
The Da Vinci Code, a novel that was subsequently turned into a film, brings to light a theory held by some conspiracists regarding the hidden truth of Jesus’ sexual involvement with Mary Magdalene. In the movie, Robert Langdon, a Harvard symbologist, while evading arrest, seeks to solve the murder of his acquaintance, coming across an…
Jerusalem is a sacred city within the teachings of the Roman Catholic Church, and its loss to the Muslims has been argued by many historians to be the reason for the initiation and perpetuation of the eight crusades, as Jerusalem is where the Crusades were primarily focussed[1]. However, it is easy to disagree with such…
As modern society advances in technology, science and philosophy; many new theories and methods of music education evolve. Learning music theory is a method of music education which is developed by Edwin E. Gordon who is a well-known researcher, teacher, author, editor and lecturer (GIML). Music Learning Theory is a process by which Gordon explains…
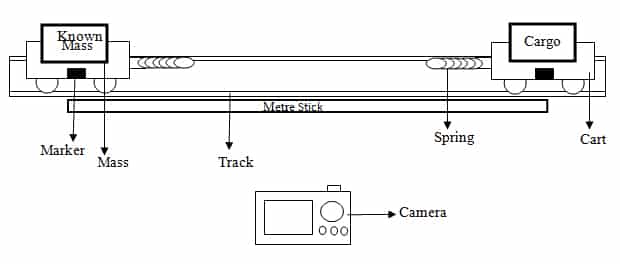
Abstract The purpose of this lab will be to determine the mass of the cargo carried on a low friction cart by analyzing its momentum during an elastic collision. The momentum will be calculated by recording and analyzing a video, in LoggerPro3.6, of an elastic collision with two carts, one with the cargo and one…
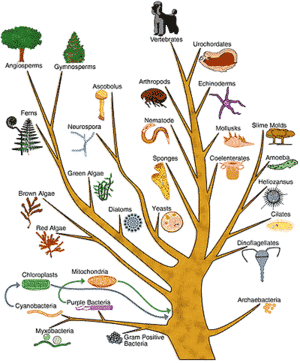
Patterns in Macroevolution Fossils Trace of any organism that lived in the past 99% extinct, used as evidence for evolution Law of Succession: resemblance between living and fossil forms in the same region Relative Dating Fossils formed in sedimentary rock in which the sediments form layers that differ in colour, thickness and composition Principle of…
Properties The speed of light is measured through the equation: v = λ f. However, it turns out that when light is reflected off a surface its speed stays the same. This was first proven by Sir Isaac Newton. Under the assumption of perfectly elastic collision, the laws of reflection follow from the laws of…
Hume’s empiricism asserts no idea without a corresponding sense impression. Therefore we cannot have a concept of something we’ve never experienced before. For example: I have an idea/concept of an apple in virtue of the fact that I’ve perceived an apple many times before. Do we have an idea of an enduring self? “[F]rom what…
What is the essential difference between belief, knowledge or true understanding? How can it be defined, what are its origins, and how is it attained? These questions are addressed in the subject of epistemology, the theory of knowledge. Much of the framework for developments in epistemology comes from the classical Greek thinkers, primarily Plato. Plato…
Substance can be most directly defined as what something is. Man is a substance, a horse is a substance and a rock is a substance. Going in-depth of the substance one is introduced to a secondary substance which is when something is in essence. For example, man has certain attributes to accentuate a man’s individuality.…
“Why does Plato compare ordinary human existence to that of chained prisoners in a cave?” The Allegory of the Cave is an allegory to evaluate a journey from darkness to light as the mind moves toward the Forms. The “cave” is considered the world of the five senses meaning we acquire our opinions through the…
As millions of tons of organic compounds find their way into the water systems of the world, the environmental problems that result are colossal. This negligence might not affect the environment directly, but they have long-term effects. Some of these problems include: Heavy metal accumulates in lakes and ponds nearby industry, and this build-up is…
In Aristotle’s previous extract, he explained the notion of the soul as a separate entity distinct from the body. This troubled Christian philosophers-theologians for they wanted to re-unite Aristotle’s philosophy with the doctrines of the church. In the “Summa Theologiae” one can see that there are pieces of Aristotelian philosophy like the description of the…