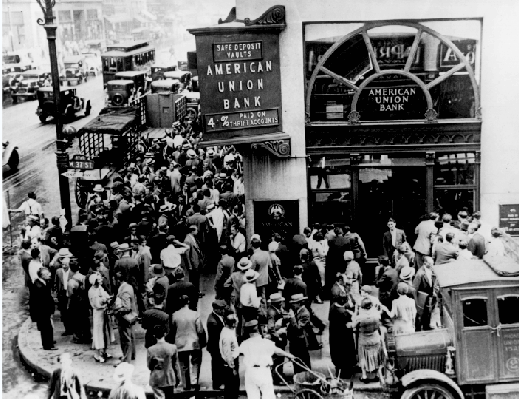William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
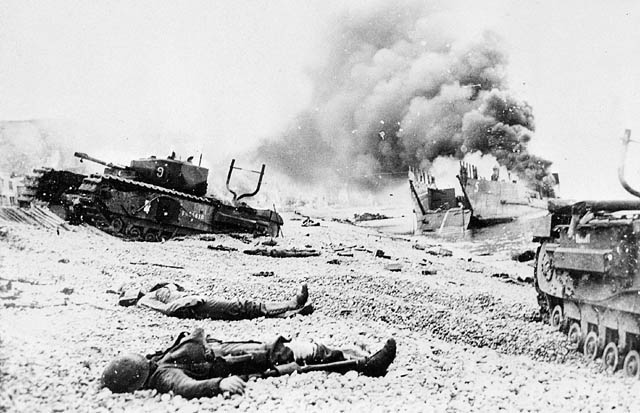
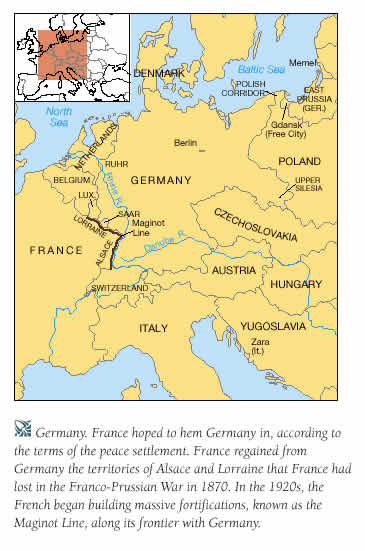
Winston Churchill and Allies under intense pressure to “do something” to relieve pressure on Soviet Union – “Operation Jubilee” was to be a quick raid: – Gather information, test tactics for a later invasion, worry the Nazis – Aug. 19th, 1942 6000 troops land in France (5000 are Canadians): – 900 die on beaches –…
ECONOMIC PROBLEMS (INFLATION) Instead of taxing its people to finance WWI, Germany had borrowed the money. Thus it had burdened its citizens with a huge debt. To payoff this debt after the war, the German government simply printed more money. This was done even though the country’s industry, agriculture, and commerce were not expanding because…
Soldiers in World War One fought under terrible conditions and were often slaughtered in useless attacks – yet millions volunteered to go. Why? 1) Patriotism and Nationalism A strong sense of national pride made men feel that it was their duty to fight. 2) Honor and Glory Many men saw the war as a…
The ‘Great War’, which began on 28 July 1914 with Austria-Hungary’s declaration of war with Serbia, was the first truly global war. It began in Europe but quickly spread throughout the world. Many countries became embroiled within the war’s first month; others joined in the ensuing four years, with Honduras announcing hostilities with Germany as…
Digging In- Troops on both sides dug deep trenches/ditches in the ground for protection. Trenches were about 2 meters deep by 1.5 m wide No-man’s-land- A neutral territory between the allies and the enemy; it was suicidal to be caught in no-man’s-land “Over the Top”- An advance frontal attack over the trenches and across no-man’s-land…
GAS ATTACKS AT YPRES “I have never been in a battle — and I have been in many — where the men were suffering in such numbers that their crying and groaning could be heard all over the battlefield.” Anonymous Soldier Canada’s first major battle in the war, near ancient city of Ypres in Belgium…
All Wet – Describes an erroneous idea or individual, as in, “he’s all wet.” Applesauce – an expletive; same as horsefeathers; as in “Ah applesauce!” Bee’s Knees – An extraordinary person, thing, idea; the ultimate Berries – That which is attractive or pleasing; similar to bee’s knees; as in “It’s the berries.” Big Cheese –…
UNEMPLOYMENT In 1930 Canada had 13% unemployment; by 1933 it was 26% (fell back to 13% when WWII broke out) Between 1929 and 1933, 1 in 5 Canadians depended on government relief for survival In Saskatchewan, income dropped by 90% forcing 66% of the rural population onto welfare no severance pay or unemployment insurance to…
There are various explanations for the causes of the great depression that started in 1929. Some of the most likely causes are given below: 1. OVER-PRODUCTION AND OVER-EXPANSION During the decade of the Roaring Twenties, many industries expanded their production beyond demands. Much money was spent adding factories and building new ones There was an…
Richard Bedford (R.B.) Bennett replaces King as P.M. in 1930 Bennet promises work for all, $20 million for emergency funds and to deal with foreign trade policies His policies did little to help the economic conditions in Canada Bennett set up relief camps for single unemployed men Men worked cutting brush and building roads for…
During the time period of 1920 to 1933, the governments of the United States of America and Canada made the manufacture, distribution, and sale of alcoholic beverages illegal. This was meant to decrease crime rates in both countries. Instead, of their dream of a crime-free society, both governments got more than they could handle. This…
August 6 and 9, 1945 At 2:45 in the morning of August 6, 1945, an American B-29 bomber flew north from Tinian Island in the Marianas toward Japan. Three and a half hours later, over the city of Hiroshima, the Enola Gay dropped an 8,900-pound atomic weapon from its specially modified bomb bay. Two thousand…
CAPITAL LETTER The beginning of a sentence Proper names of people and places Canada, Rome, Toronto, Sandalwood Heights, Teddy, Toronto General Hospital Titles Queen Elizabeth, Captain Torres, Miss Butler The first letter of each word in a title Just Lather, That’s All The Fall of a City For the word “I” The date, days of…
STEP ONE: COMMUNICATION Circle ALL spelling and grammar errors. If there are any errors in terms of the correct format of quotations and citations, indicate the error and what the problem is. Check the structure of the body paragraphs: ensure they are in the SQA format. STEP TWO: THINKING Carefully read all of the ANALYSIS…
Tragedies present tales of suffering and calamity, often involving violence and death; though in Greek tragedy, the violence and death always occur offstage, in Shakespearean tragedy, the deaths sometimes take place on stage. Tragedies lead to the deaths of “exceptional” people such as royalty, nobility, etc. The idea is that the higher a person is…
1. Use commas to separate items in a series of three or more. e.g. The required subjects in this program are math, physics, and English. Tom went to the movies, Jan and Jasmine went to play pool, and I went to bed. Exercise: Insert commas where necessary in the following sentences. 1. The five largest…
THEMES 1. Archetypal journey from innocence to experience – the innocent stage: a group of young boys (children represent innocence and purity); the island at first seems like a beautiful paradise/Garden of Eden. – the experienced stage: what they go through (“the fall from grace”) and the devastating, irrevocable changes that result. 2. Civilisation vs.…
You are to select one of the following topics and write an academic, formal, literary essay with an introduction, body paragraphs, transition paragraphs and a conclusion. It should be no more than five typed pages (double spaced-including quotations) 1. “Robert Ross comes riding straight towards the camera. His hat has fallen off. His hands are…
Literary analysis is a critical response to a literary text in the form of a critical essay or an oral commentary. It includes a thorough interpretation of the work. Such analysis may be based on a variety of critical approaches or movements, e.g. archetypal criticism, cultural criticism, feminist criticism, psychoanalytic criticism, Marxist Criticism, New Criticism…
Anacoluthon – In rhetoric, a break or change in direction in a speech, often signaled by a dash. Example: “I was listening to the news – this man he’s a company director in London – the police arrested him.” Anadiplosis – A word repeated for effect. Example: “Victory at all costs, victory in spite of…