William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
Since, the time of Sir Isaac Newton, the mysterious force of gravity has intrigued many physicists for centuries. The classical anecdote of the apple falling on Newton’s head led Newton to propose that some mysterious force must be pulling that apple downwards. While this was a great leap forward in the field of physics, Newton…
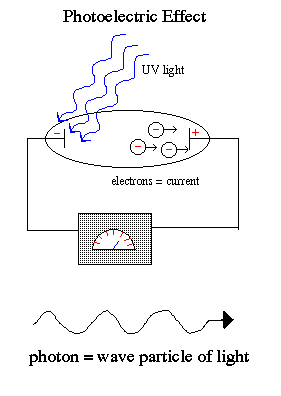
The properties of light have been understood by physicists to be completely fundamental to our understanding of the universe, however defining these properties have proven difficult to elucidate. What is light? What is light composed of? Does light obey classical physics? These questions are important to answer when considering physical phenomena that involve light. One…
Supernovas can occur in two different and distinct ways. One of the ways in which a supernova can be triggered is through the instantaneous ignition of a nuclear fusion reaction in a degenerate star (star at end of its life). For example, a white dwarf, in a binary system, may accumulate material from that companion…
Black holes are regions of space-time that prevent anything, including light, from escaping. The reason for this is that black holes are extremely dense and so the escape velocity required to escape the black hole must be huge. It should be made clear that a black hole is a distortion of space-time (Einstein had described…
Queen Elizabeth was born on September 7th 1533. She was queen regnant of England and Ireland until the 17th of November 1588 until the day of her death. She is the daughter of King Henry VVI and was born naturally into the royal succession. Her mother who is Anne Boleyn had been executed when Elizabeth…
Intoxication Intoxication is when a person’s mental state is impaired as a result of taking alcohol or drugs. In general, intoxication is not a valid excuse as a defence for crimes. The law holds people responsible for putting themselves in a state of intoxication and for the consequences of their actions while in this state.…
Purpose: The purpose of the lab was to dissolve Copper salt in water with an excess of Aluminum. The mass of the Copper formed was to be determined and the percentage yield was to be calculated. Related theory A chemical reaction is the change of substance into a new one that has a different chemical…
Background: The Aboriginal Peoples Television Network (APTN) is a television channel that broadcasts programs “made by, for and about Aboriginal Peoples”. “APTN is available in approximately 10 million Canadian households and commercial establishments with cable, direct-to-home satellite (DTH), telco-delivered and fixed wireless television service providers. The network launched its high definition channel APTNHD in the…
Ever since the first explorers came to Canada, their goal was to expand culture and gain wealth for their mother country. When the British won/took the french colonies, they tried to build on what France had already done. The outcome to this, that still exists is a flourishing French population where the French colonies had…
Colonial history in Canada has evolved from a very bias country condemning First Nation peoples to be inferior to Europeans to what Canada is now, a country recovering from past mistakes and recognizing the mistakes the whole country has made to all indigenous people. Throughout the years Canadians have become more educated about the lack…
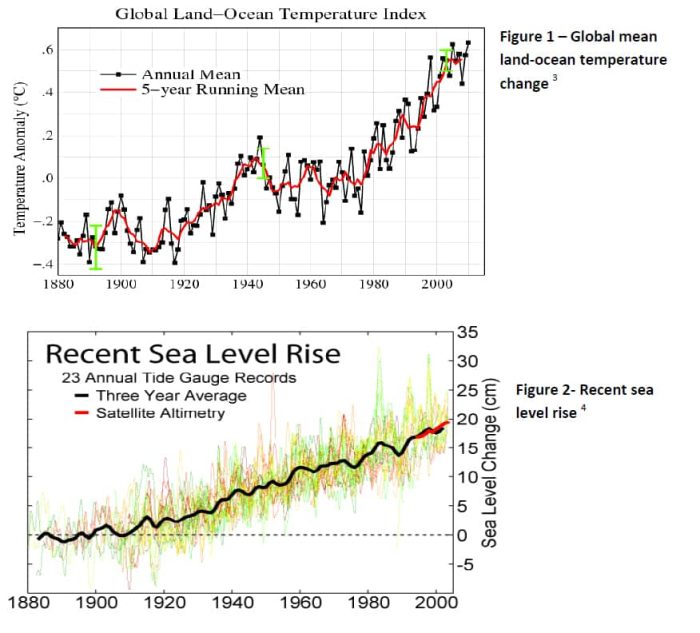
The global average air and ocean temperatures have been gradually increasing from 1880-2010 (Fig.1) This increase in temperature melted a massive amount of ice and snow globally which ultimately, caused the global average sea level to also rise (Fig.2). The Earth’s average surface temperature rose by 0.74 ± 0.18°C over the period 1906–2005. Global average…
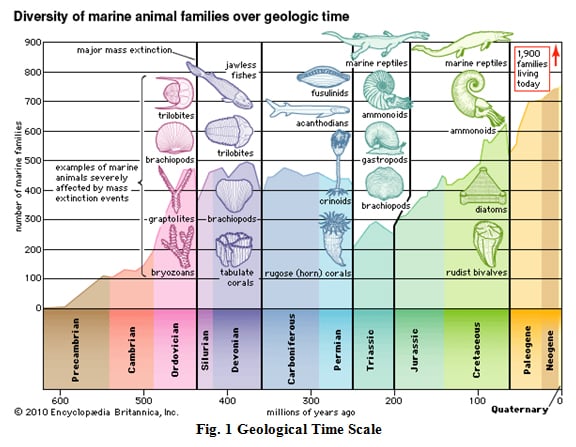
The Ordovician period is placed between 488.3±1.7 to 443.7±1.5 million years ago.1 It is preceded by the Cambrian period and is followed by the Silurian Period as seen in Figure 1.1 Initially, only these two periods existed, until 1979 when Charles Lapworth defined the Ordovician period as a period of its own based on fossil…
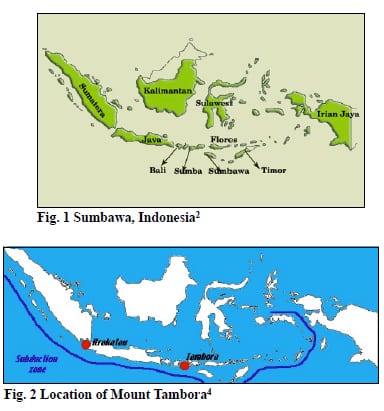
Mount Tambora, is an active stratovolcano famous for its eruption in 1815 which was considered one of the most explosive volcanic eruptions in Earthʼs history. A stratovolcano is a volcano characterized by its steepness and periodic explosive eruptions and quiet eruptions. It is also known as a composite volcano because it is composed of layers…
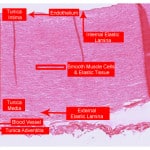
Aorta Basophils Cardiac Muscle Cardiac Muscle Longtudinal Cerebellar Cortex Cerebral Cortex Spinal Cord Eosinophils Epiphyseal plate Femoral Artery Femoral Vein Howship’s lacunae Jejunum lamina propria Liver Lymph node Lymphocyte Monocyte Spinal cord (silver) Neutrophil Pacinian corpuscle Peripheral Nerve Peripheral Nerve 2 Respiratory Epithelium Spinal cord (silver) 2 Simple Cuboidal Epithelium Simple Columnar Epithelium Skeletal Muscle…
Worms do many of the things humans do to survive. They breathe, move around, reproduce, and eat. Worms have the epidermis; which is like our skin, a layer of nerve tissue, which acts like our sense of touch. Instead of having just one heart, they have five hearts. These hearts regulate blood flow and produce…
Research question: All organisms have activities, organisms use energy to accomplish activates. Organisms eat food to gain energy, this energy is stored for later use. Since humans are organisms we eat food to gain energy. Which food of the same category gives us more energy? Hypothesis: Since fat is the main reserve that is burnt…
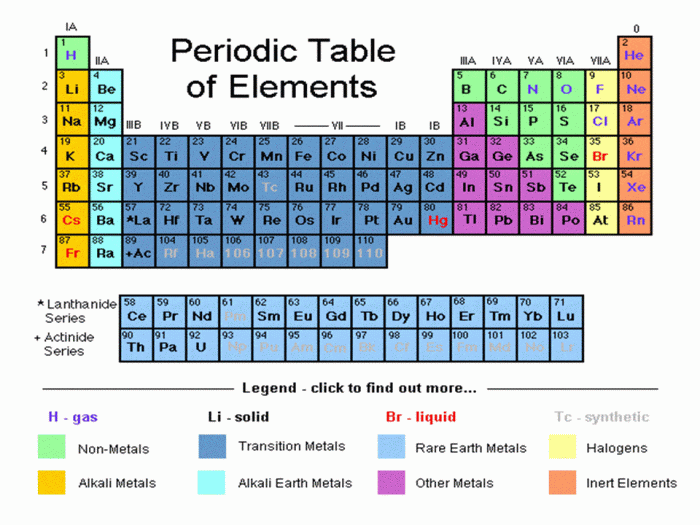
Metalloids: Are the least common type of elements, their properties are a mix of nonmetal and metal properties. The metalloids are hybrid elements. Perhaps the most important characteristic of metalloids is that they partially conduct electricity for semi-conductors. Nonmetals: Are opposites of metals, that’s why they are called nonmetals (not metals). They are not malleable…
Quote: “It will have blood they say; blood will have blood.” (3.4.123) Speaker and Audience: Macbeth is speaking to his wife, Lady Macbeth Context: Prior to Macbeth saying this quote of key importance in the tragedy, he witnessed the ghost of Banquo, whom he murdered so that he wouldn’t be found guilty of Duncan’s murder.…
The antagonistic force of evil has been a common theme in society and literature, it can be manifested into various forms, functions, and interpretations. Evil follows the law of relativity and thus differentiates from each point of view and situation. Although evil is not truly existent, necessarily, classical literature manages to portray evil in supernatural…
What caused Macbeth’s inevitable catastrophe? Was it what he experienced from a series of external forces, or his choice of reaction to them? One may believe that Macbeth was under the mere perception of free will or he was controlled by other deities. This is simply not true. Macbeth was, unfortunately, a victim of his…