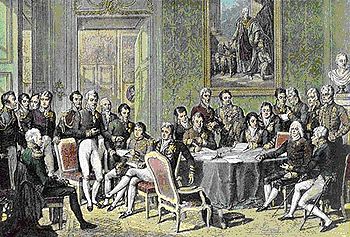William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
Key Players of Congress of Vienna The “Host” Prince Klemens von Metternich (Aus.) Foreign Minister, Charles Maurice de Tallyrand (Fr.) Tsar Alexander I (Rus.) King Frederick William III (Prus.) Foreign Minister, Viscount Castlereagh (Br.) Main Objectives Its job was to undo everything that Napoléon had done: Reduce France to its old boundaries -> frontiers were…
Legal Issues that arise out of divorce Custody of children – who gets the kids? Division of property – who gets the house? Spousal support – which spouse pays which spouse? Child support – who pays for the kids? How to get a divorce. There is NO SUCH THING as a contested divorce in most…
Origins of Moon Theories Three theories on origin of the Moon: Earth and moon formed simultaneously, with moon orbiting around the earth. Early earth was spinning so fast that a chunk of it broke off from it and spun of into orbit and became the moon. Moon formed elsewhere in solar system and was later…
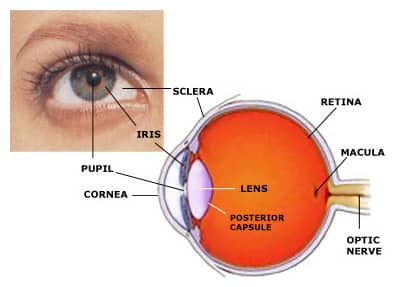
Parts of the Eye The human eye is like a camera: Iris- like the diaphragm of a camera it controls the amount of light entering. It is the coloured part of the eye and opens and closes around a central hole to control the light entering the eye. Pupil- this is the hole in the…
Where Mountains Form? A mountain is a large mass of rock that rises a great distance above its base. Are formed due to tectonic activity – due to convergence of plate boundaries Most of the world’s mountains are formed in long belts due to the whole side of plates crashing into other plates A mountain…
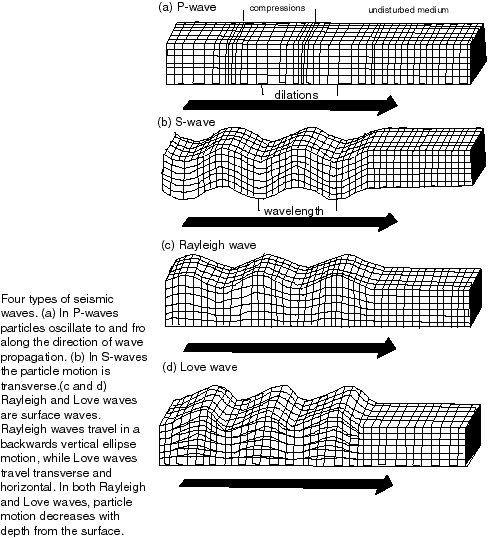
Are caused by the shaking or trembling caused by the sudden release of energy Usually associated with faulting or breaking of rocks – cracking of the plates also called faults. Continuing adjustment of position results in aftershocks Unstable Earth The Earth’s crust is subjected to huge forces Very large forces can fracture the rock This…
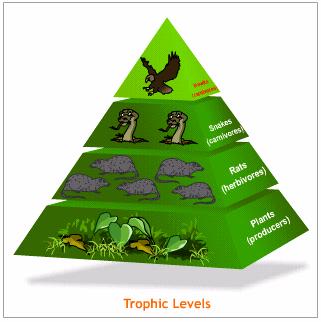
Organisms can be classified into trophic (feeding) levels depending on how they get their energy. Organisms that get their energy from nonliving sources (sun, organic matter) are called autotrophs (producers) and make up the 1st trophic level. Organisms that get their energy from other living things are called heterotrophs (consumers). Heterotrophs that eat autotrophs make…
4 Types of Pesticides Herbicides : kills plants Insecticides : kills insects Fungicides : kills fungi Bactericides : kills bacteria First-Generation Pesticides inorganic biocides (eg. Metals such Lead, mercury, arsenic, cyanide) Found to be toxic to humans, polluted water and soil and were not biodegradable (not able to break down naturally). Materials from a non-living…
Chapter 2: the No-Daddy Blues Chris Gardner, hoping to get Freddie to like him, does well in school – a haven where he seemed to thrive at learning and in social interactions. His early exposure to books paid off, and with his Momma’s continuing encouragement, he quickly mastered reading. While his accomplishments as an elementary…
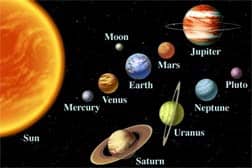
Our solar system is divided into two sections, the first section being the inner planets consisting of Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. The inner planets have rocky crusts, dense mantle layers, and very dense cores. The second section consists of Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune, and Pluto. Except for Pluto, the outer planets are gaseous with…
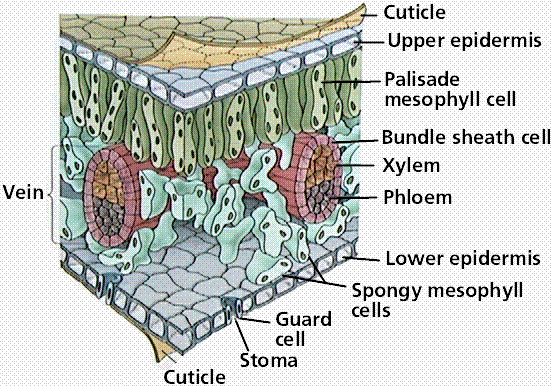
Plants are organized into two sections: 1) Shoots – stem and leaves 2) Roots Stems: Support leaves Transport water and minerals to leaves Transport sugar to the leaves Two main types of stems 1) Herbaceous – green and soft Contain vascular bundles o Collections of xylem (water) and phloem (carbs) § Can be scattered (monocots)…
The ledger should be balanced after each full accounting entry. Periodically it is necessary to check the accuracy of the ledger. This is done by doing a trial balance. A trial balance is a listing of the account balances in a ledger. You must add up all of the debit balances, and all of the…
The memory fades. Willy laments to himself and Happy that he did not go to Alaska with his brother, Ben, who acquired a fortune at the age of twenty-one upon discovering an African diamond mine. Charley, having heard the shouts, visits to check on Willy. They play cards. Charley, concerned about Willy, offers him a…
Willy is lost in his memories. Suddenly, the memories of his sons’ childhood come alive. Young Biff and Happy wash and wax their father’s car after he has just returned from a sales trip. Biff informs Willy that he “borrowed” a football from the locker room to practice. Willy laughs knowingly. Happy tries to get…
Themes The American Dream Is the capitalist belief that if you work hard enough you can be a success in America (the same is true for those of us living and working in Canada). However, the success that the dream aspires to is based on money and power. In Willy’s mind it is also linked…
10. Establish a proper study area. We recommend the kitchen or dining room table. This area should be free of distractions such as the television. Hint – never use your bedroom as a study area. A study area should never be too comfortable. 9. Make studying a regular routine in your day. “Motivation is what…
THE HERO (ES) All of Shakespeare’s tragedies have a tragic hero or ‘protagonist’ who is put into a situation of conflict which he must resolve. A combination of bad luck and misjudgment leads to the hero’s death. He is often a man of high social standing: Romeo and Juliet are both wealthy citizens of Verona…
Shia Are believed to be the descendants from Muhammad through his daughter Fatima and son-in-law Ali. It is believed that they are the best source of knowledge about the Qur’an and Islam This is the key difference between followers of Muhammad’s family and descendants from the followers of Caliph Abu Baker Sunni They are the…
Comments Documentation Comment Statement Comments /** * */ E.g., /** This is a sample comment * that would span * multiple lines */ // // This is a sample single line comment Primitive data Type int E.g., int sumOfNumbers; double E.g, double average; char E.g., char singleChar; boolean E.g., boolean isBig; Declaring Variables <Visibility> <type> …
Fallacy: Is a hypothesis that has been proven false but is still accepted by many people because it appears, at first glance, to make sense. The Fallacy of Composition A mistaken belief that what is good for the individual is automatically good for society as a whole. Eg: Clearing the trees from Crown land will…