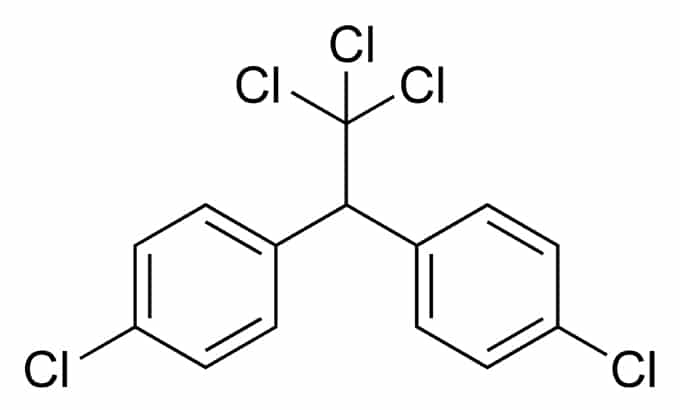
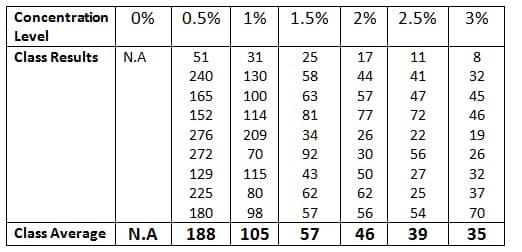
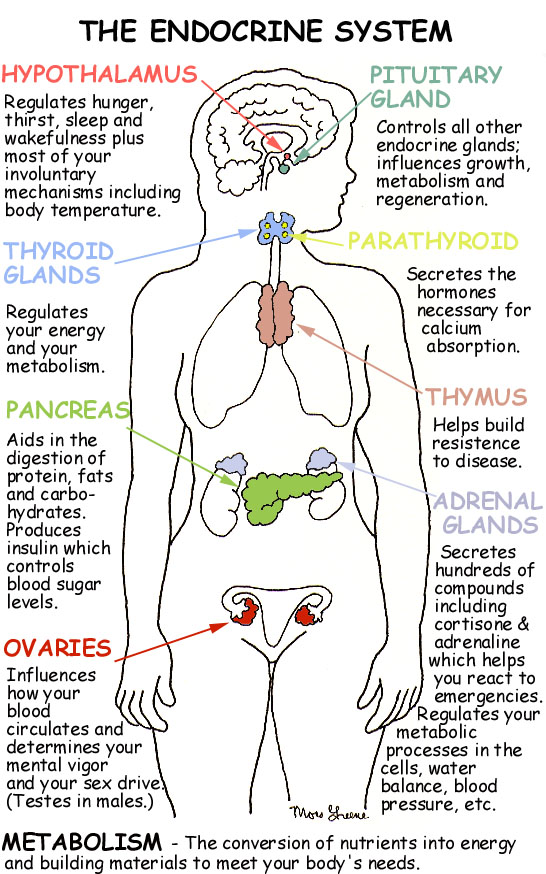
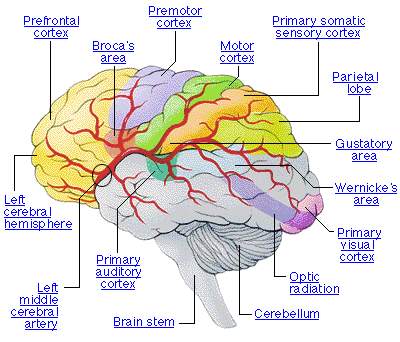
Major Hormones: Origin, Target, Function
HORMONE GLAND ORIGIN TARGET TISSUE FUNCTION Adrenocorticotropic Pituitary gland (anterior) Adrenal cortex Triggers secretion of hydrocortisone from the adrenal gland Growth hormone Pituitary gland (anterior) Throughout body Stimulates growth and development Follicle-stimulating hormone Pituitary gland (anterior) Sex glands Stimulates female egg maturation and male sperm production Luteinizing hormone Pituitary gland (anterior) Sex glands Stimulates female…