William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
Origins Christianity began in the land of Palestine (Israel), primarily in Galilee and Judaea. Founded by Jesus of Nazareth (c. 4 BCE – c. 29 CE), who has left no writings of his own. Jesus began teaching and healing around the age of thirty. Jesus was born a Jew who prescribed changes within Judaism. Jesus…
The Great Schism 1054 It is often stated that the Eastern Orthodox Church and the Roman Catholic Church was founded at the time of this great schism. That is false. The One Holy Catholic and Apostolic Church was ruled by five patriarchs: those of Rome, Constantinople, Antioch, Alexandria, and Jerusalem, each having authority over bishops…
Within a few generations of Jesus’ death, Christianity had spread from the middle east to Greece and Rome 325 CE, the Emperor of Rome organized a council of religious leaders at Nicea (a city in modern-day Turkey) The idea was to decide on the official beliefs of the Christian Church. This meeting produced the Nicene…
There is one God who is the creator of everything God is immaterial (without form) God governs the universe with honour and justice Therefore, humanity has an obligation to worship God Jewish Practices and Rituals The Synagogue: Place of worship and study Sometimes called “Shul” (Yiddish for school) The Torah Scroll: Holy book Most sacred…
Smallest (about 14 million) of the major world’s religions Why study it then? – Long history of persecution that we can learn from, and Judaism has made a huge contribution to Western philosophy and religious thinking. Oldest of the Abrahamic faiths, dating back about 4000 years Shares a history and mythology with Christianity and Islam…
The Buddha chose the symbol of an eight-spoked wheel to represent the path to Nirvana The center of the wheel represents Nirvana, the only fixed point Just like the spokes are needed to let the wheel turn, Buddhists need to follow each step of the path to reach Nirvana Each path is used not individually,…
The Buddha observed that no one is free from death and unhappiness (dukkha) Buddha looked for the source of that unhappiness (like a doctor looking for the source of an illness) These are the four noble truths, and they are central to understanding Buddhism Some people see great wisdom in these truths; others find them…
School Geography Thoughts Rituals Theravada Sri Lanka, Thailand, Laos, Cambodia “the way of the elders” Conservative Do not worship Buddha as a god. Meditation Mahayana China, Vietnam, Korea, Japan “the greater vehicle” Older forms of the religion. Liberal Heavens are populated with Buddha or divinities to whom people can pray. Bodhisattvas. -the buddha is the…
Most Buddhist devotions are not performed in a temple, instead people have a place of worship in their homes The temple is usually reserved for important celebrations Puja – showing reverence for holy beings by bowing, making offering and chanting (e.g. showing reverence for a Bodhisattva – a person who has attained Nirvana but chooses…
History · Their theology has had a great impact on Judaism, Christianity and other later religions, in the beliefs surrounding God and Satan, the soul, heaven and hell, saviour, resurrection, final judgment, etc. · It is one of the oldest religions still in existence, · It may have been the first monotheistic religion. · The…
History Jains believe that their founder, Vardhamana Mahavira (599-527 BCE) is the last of 24 holy teachers who came to teach the way of self mastery. Mahavira is not looked at exactly as a religious founder, but rather as a teacher who came to re-establish what had previously been taught Mahavira was a jina or…
Confucius was a contemporary of Lao Tzu, they had similar philosophies (e.g. the importance of harmony and balance) Confucius mastered the six arts: ritual, music, archery, charioteering, calligraphy, and arithmetic His father died when he was a child, his mother died when Confucius was in his early 20’s. After this, he became a teacher and…
Origins -Archaeological evidence suggests humans came to North America approximately 14,000 years ago, across the Bering land bridge -Most First Nations creation stories suggest that people have simply always been here (e.g. The Haida people’s Raven story, Iroquois people’s turtle island story Beliefs -Many First Nations people practice Christianity – a reminder of the impact…
Religion as Belief Belief in what? The truth and existence of God(s) and/or Goddess(es) Cosmic Order? Afterlife? “Something out there” Truth contained in religious texts, doctrines (beliefs), and/or ethics? Why do people believe? What convinces them of their belief? What does this sort of belief do for the believer? Religion as Rite (practice) Sacraments, prayer,…
Humans are very reliant upon electricity. Think back to the blackout of August 2003 and recall how whole cities were shut down. Since we rely on electricity so much, it’s important to produce as much of it as possible and conserve it whenever we can. All energy sources are either renewable or nonrenewable. A renewable…
– Your home is one large electric circuit that is wired in parallel (multiple electron paths) – Today we’re going to look at how electricity is delivered to your homes. HOW ELECTRICITY FLOWS TO YOU – Electricity flows to every home through high-voltage wires. The wires are either above ground and span over cities in…
– As the human population keeps increasing (it’s over 6 billion people right now), we keep requiring more and more energy. – Using too much energy places stress on our energy production systems and may cause blackouts when we need the energy the most. HOW DO WE USE ELECTRICITY? – In order to conserve (save)…
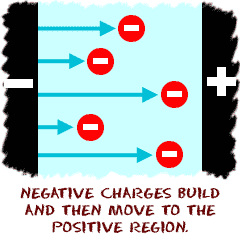
– All electrical devices have an electric circuit, also known as a path for electrons to flow. – All circuits have at least four parts: An energy source (we’ll be using batteries which are also called “cells”). An electric load (an electrical device used to convert electricity to another form of energy. We’ll be using…
Everything in the universe is either matter or energy. We studied matter in the Chemistry unit; it is everything that we can touch, smell, taste, and see. Energy is the ability to do work and it comes in many different forms. Forms of energy include kinetic energy (energy of movement), light, heat, solar energy (from…
In the mid-1800s there were 64 known elements (today there are over 116 elements). Scientists kept having difficulties organizing the information about the 64 elements. They kept trying to organize them but found no pattern between them. Many chemicals have very similar colors, luster, and conductivity of electricity and heat. Scientists were able to classify…