William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
The quantity of energy associated with the formation of one mole of a substance from its elements (in their standard states). The standard states (at SATP) of most elements are solid, except for the gaseous diatomic molecules, H2, O2, N2, F2, Cl2, and the two liquid elements Hg and Br2. These energies can be looked…
Serbia Serbia of 1914 has been described as an aggressive, backward, and domestically violent nation. Part of the Austrian-Hungarian empire. This empire included five religions and more than a dozen languages. Serbia was one of the chief sources of trouble for Austria-Hungary. Balkan region of Southeastern Europe controlled by A.H. Many of these nations looking…
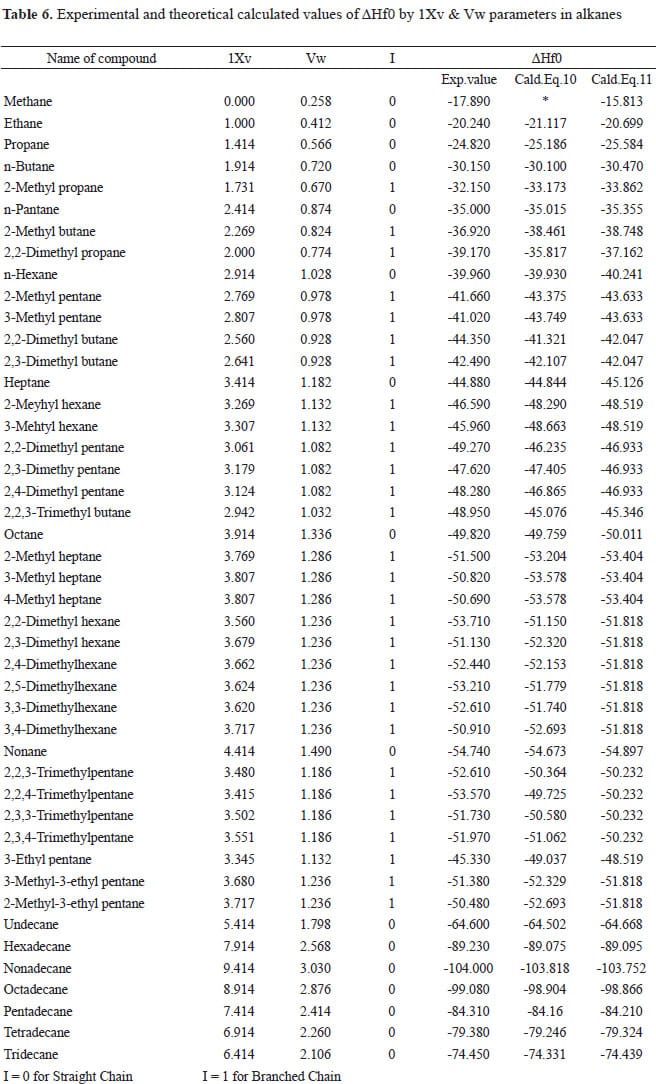
Created by General Count Alfred von Schlieffen, December 1905 Plan worked in the event of an attack on France one Russia had started to mobilize forces near the German border. In 1905, Shlieffen was chief of the German General Staff. Schlieffen believed that the most decisive area for any future war in Europe would be…
Nearly two-thirds of all people with diagnosable mental disorders do not seek treatment. –Surgeon General’s Report on Mental Illness What is mental illness? Mental illness is a disorderly functioning of the mind Early Explanations Demonology-thought that an evil being possessed a person; use exorcism to cast out evil spirits (e.g. chanting, elaborate prayer, force to…
Temperature Most seeds need a certain degree of warmth to germinate (sprout). Most plants have an optimal (best) range of temperature for growth. Higher: Plants have smaller leaves, thicker cuticles, and wilt is more likely to occur. Lower: Grow lower to the ground, have shorter life cycles, and dish-shaped leaves. Temperature affects moisture and nutrient…
RUDOLF HESS: DEPUTY TO ADOLF HITLER 1894—1987 Acting as Hitler’s private secretary, he transcribed and partially edited Hitler’s book Mein Kampf, and eventually rose to deputy party leader and third in leadership of Germany, after Hitler and Hermann Göring. He would introduce Hitler at Nazi party rallies and held the official title of “Deputy Fuhrer”…
Biological (Medical) Model The mind’s activity depends on the brain whose composition is genetically determined Still acknowledge influences of environment and learning Genetic influences on anxiety and depression Brain structure different in individuals with schizophrenia- process information differently Therapy: Pharmacological treatments (medication) Behavioural Model Focuses on what people do rather than on brain structures and/or…
Typically emphasizes exposure as well as changing problematic patterns of thinking Typically involve- 10 individual or group sessions with a therapist plus homework Has been shown to produce significant improvements Has been combined with drug therapy Agoraphobia: Fear of not being able to escape from a public place if they have a panic attack The…
Debates concerning multiculturalism are sure to spark controversy. In today’s modern societies multicultural views are seen as progressive and those who oppose these ideas are frequently seen as archaic and ignorant. But what is multiculturalism by definition; does it even have one? The sensitive debates surrounding multiculturalism have only emerged in political discussions in recent…
Becoming Human There are two basic approaches to understanding how we develop our personalities – broadly defined as an individual’s relatively stable pattern of behaviours and feelings – and become members of the larger society These are the biological approach and the environmental approach, traditionally referred to as the nature vs. nurture debate o The…
Teams and Teamwork: Decision Making in Teams Decision making – is the process of making choices among alternative courses of action. How Teams make Decisions Decision by lack of response: one idea after another is suggested without any discussion taking place. Decision by authority rule: the leader, manager, committee head, or some authority figure makes…
Sex and Gender Roles Sex – a determination of male or female on the basis of a set of socially agreed-upon biological criteria Gender – social distinctions between masculinity and femininity The Biological Female and Male? Problematizing the sex/gender distinction, and the category of sex itself, is the assertion that our bodies are absolutely separate…
Avenues to Knowledge and Reasoning The kinds of research questions you will ask will always depend on the theoretical perspective from which you are working Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches Quantitative refers to numerical data involves converting aspects of social life into numbers and determining whether a significant relationship exists between sets of numbers Qualitative refers…
What is Culture? Culture is generally regarded as a complex collection of values, beliefs, behaviours, and material objects shared by a group and passed on from one generation to the next There is nothing good or bad about culture – it just is what it is Origins of Culture and Its Defining Features No one…
What is a Minority? Minority – a definable category of people who are socially disadvantaged Membership in a minority group has two components: the group lacks social power, and it is definable as being distinct from the majority Majority – a definable category of people who are socially advantaged For sociologists, the defining feature of…
Species: Latin word meaning “kind” Speciation: The origin of new species Macroevolution: The evolutionary changes above the species level eg. The appearance of feathers during the evolution of birds from one set of dinosaurs Anagenesis – one species over time becomes another species Cladogenesis– one species, over time, splits and becomes two species Morphogensis– look…
Theories in sociology are abstract, general ideas that help organize and make sense of the social world Epistemology Philosophical Roots of Classical Sociological Theory Thomas Hobbes (1588-1679) Suggested that people are responsible for creating the social world around them, and thus society could be changed through conscious reflection Was one of the first theorists to…
The chemical reactions of metabolism are reversible, and they, too, would reach equilibrium if they occurred in the isolation of a test tube. Because systems at equilibrium are at a minimum of G and can do no work, a cell that has reached metabolic equilibrium is dead. A cell in our body is not in…
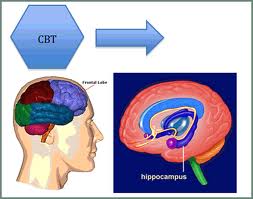
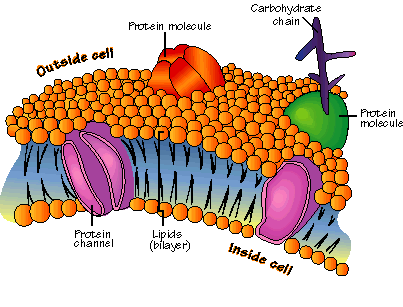
Selective Permeability: Allows some substances to cross it more easily than others. A phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule, meaning it has both a hydrophilic region and a hydrophobic region. Fluid Mosaic Model: The membrane is a fluid-structure with a “mosaic” of various proteins embedded in or attached to a double layer (bilayer) of phospholipids. The…
Living systems increase the entropy of their surroundings, as predicted by thermodynamic law. We can trace the ancestry of the plant kingdom to much simpler organisms called green algae. However, this increase in organization over time in no way violates the second law. The entropy of a particular system, such as an organism, may actually…