Tutor and Freelance Writer. Science Teacher and Lover of Essays.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2024 | Creative Commons 4.0
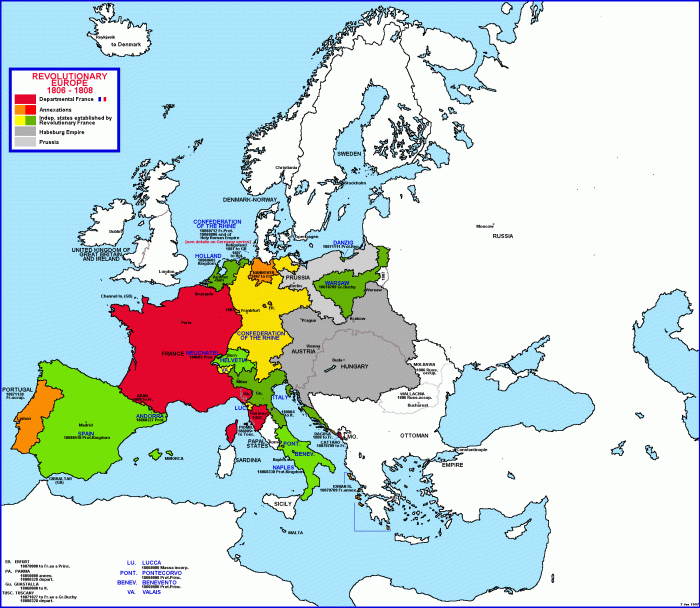
Treaty of St. Germain Officially signed on September 10, 1919 and came into force on July 16, 1920. The treaty officially registered the breakup of the Habsburg Empire, recognizing the independence of Czechoslovakia, Poland, Hungary, and the Kingdom of the Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes (Yugoslavia) and ceding eastern Galicia, Trento, southern Tirol, Trieste, and Istria.…
Why was Vietnam a so heavily divided subject amongst the American People? Vietnam was the first publically accessible war to the American public. With the invention of the television and the constant media exposure, for the first time the horrors of war was a publically accessible domain. Due to this, a ‘generation gap’ was created,…
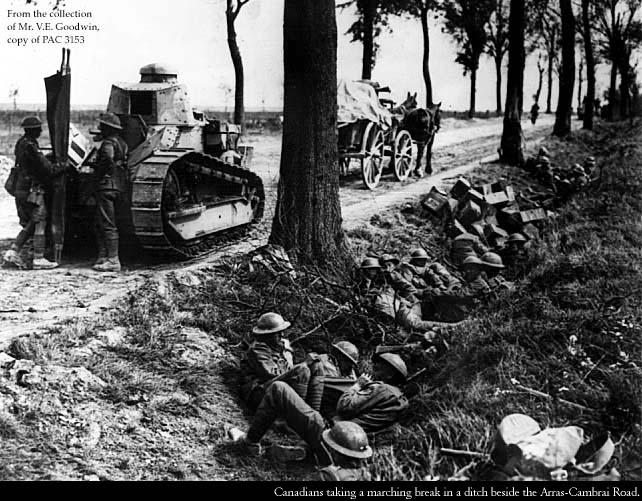
Why would Canadian get involved in a war so far away? Britain declared war on Germany on August 4, 1914. As part of the British Empire, Canada was automatically at war (where Britain led, Canada must follow). The only thing in Canada’s power was the level with which it participated. Most Canadians felt very strongly…
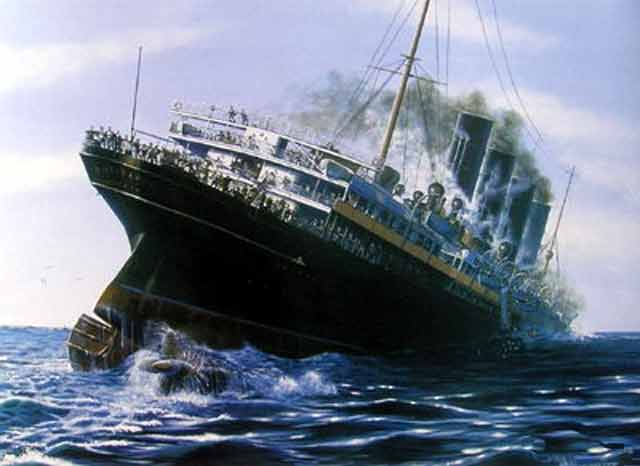
Reasons for Involvement Unrestricted Submarine Warfare: In January 1917, failed crops as well as a naval blockade caused severe food shortages in Germany. Desperate to attack back, Germany decided to establish its own naval blockade around Britain. They decided to sink any ship in the waters around Britain without warning, through the use of submarines.…
Life in the country is often viewed as a calm, quiet escape from the hustle and bustle of the big city. In the movie “Sunrise: A Song of Two Humans”, F.W Murnau depicts a comfortable, friendly country environment and a restless and loud urban setting of the early nineteenth century; a contrast which is as…
Background Info Once installed as the President, Peron proceeded to put in the corporatist principles of the GOU (Groupo de Oficials Unidos). He decided that Argentina would be divided in to three functional groups; industrialist, farmers and workers. At the peak of the hierarchy would be the state. Peron made his urban workers his most…
The secretariat of the League was divided into three main departments dealing with: Economic, financial and transit questions Social and humanitarian problems (health, drug traffic, child welfare, social work, refugees, intellectual collaboration); Legal and administrative questions (registration of international treaties, protection of minorities, mandates, slavery). The League had four ways to enforce the provisions of…
The Battle of Atlantic lasted as long as WWII itself, 1939-1945, however, it was most significant from mid-1940 to the end of 1943. To survive the war against Hitler’s forces, Britain needed imports of food, fuel and raw materials from overseas. America provided Britain with the only tools needed for its success as Britain’s successful…
Vietnam Escalation The Communist activity in Vietnam was a direct challenge to the American mission to lead the free world into the next century. Dean Rusk, who had been the assistant secretary of state for Far Eastern Affairs in both the Kennedy and Johnson administrations, making him one of the chief architects of the Vietnam…
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization – created on April 4 1949. It is the military alliance of Democratic states in Europe and North America. NATO founding members stated on April 4 1949 in Article 5, the parties agree that an armed attack against one or more of them in Europe or North America shall be…
YASSER ARAFAT He was born on 24 August 1929 in Cairo, Died in 2004. In 1958 Arafat and his friends founded Al-Fatah, an underground network of secret cells, which in 1959 began to publish a magazine advocating armed struggle against Israel. At the end of 1964 Arafat became a full-time revolutionary, organising Fatah raids into…
Leadership of Gamal Abdul Nasser, President of Egypt from 1954 to 1970 Biography Was part of the Free Officers, a group of Egyptian officers plotting to overthrow the Egyptian government (early 1950s) July 1952, he helped overthrow the unpopular government In 1954, Nasser became President: his goal was to give Egypt true sovereignty by freeing…
Russo-Japanese War in 1904-1905 Japanese established authority over Korean peninsula Koreans fought for independence but the Western blocs did not intervene until the outbreak of war in the Pacific during WWII in 1941 Cairo Conference 1943 – Roosevelt, Churchill and Chiang Kai-노다 declared support to remove the Japanese from Korea “three great powers, mindful of…
June 27, 1950- Truman announced that he would increase U.S. military assistance to the anti Communist forces and install a new permanent U.S. military mission in Saigon May 1- Truman approved $10 million of aid Truman allocated $5 million for military assistance on June 27 Additional $16 million on July 8. By the time of…
Collective Leadership 1953 After Stalin’s death, the party leaders wanted collective control so that no single leader could again dominate party and government. Following his death in March 1953, the collective leadership that emerged was made up of Malenkov (Soviet Premier), Molotov (Foreign Secretary), Bulganin (Deputy Premier), and Khrushchev (Party Secretary). The immediate problem they…
Leadership of Saddam Hussein Brief Biography Born April 28, 1937 By 19, Hussein was supporting Arab unity and joining the socialist Baath Party Involved in failed assassination attempt of Prime Minister General Abdel-Karim Qassem at 22 years of age Studied law in Egypt with degree from University of Cairo’s law school in 1962 Vital role…
Location: French Port of Dieppe (northern coast of France) Date: August 19, 1942 Nations involved: USA, Britain, Canada vs. Germany Key Figures: British Chief of Combined Operations – Louis Mountbatten, Canadian Major-General J.H. Roberts, German General Field Marshal– Gerd von Rundstedt Objectives: Allies wanted to test amphibious techniques and gather data on coastal defenses and…
The Roots if the Revolution: The Nationalities. The Russian Empire was “an unwieldy conglomeration of territories inhabited by a nationally variegated population…” (pg 174) By 1914, Russia was composed of 148.4 million people. 43.4% were Russians, 17.5% Ukrainians, 10.6% Turkish speaking people. Some people such as the Fins, Poles and the Jews had a strong…
Location: Stalingrad, Southwestern Russia Date: July 17th, 1942- February 2nd, 1943 Nations Involved: Germany, Hungary, Italy, Romania, and Croatia vs. the Soviet Union Strategy Relevant to the Battle Operation Blue: The plan was to concentrate all available forces in the southern flank of the long front, destroy the front line Russian forces there, and then…
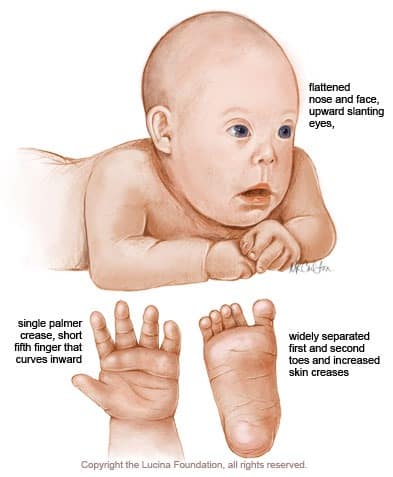
Down syndrome is a genetic and chromosomal disorder where a person has either half of or a full extra 21st chromosome. The disorder was first discovered by John Langdon Down, a British doctor, who first described the disease in 1866. Down syndrome is caused by a chromosomal abnormality which causes a replication of the 21st…