William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
Definition An eating disorder characterized by massive food binges (similar to Bulimia Nervosa) without the purging or other compensating behaviours. Characteristics Periods of eating compulsively and consuming large quantities of food until the individual is uncomfortably full, followed by feelings of guilt and shame which lead to secretive eating. Use food as a way to…
Definition An eating disorder characterized by the refusal or inability to eat which creates a state of self-starvation. Characteristics Victims have a severe distortion of body image and extreme concern about appearances. Use voluntary starvation, excessive exercise and diet pills to try and achieve idealized body proportions. Have an obsession with food and calories. Physical…
The diet business is fat and healthy. Anyone who swigs diet soda, works out regularly or subsists on fat-free food, is feeding this multi-billion dollar industry. Annual diet industry revenues have grown from an estimated $100 million in the 1950s to $50 billion in the 1990s. The industry encompasses all products and services that claim…
Practice Healthy Eating Habits One of the good points about many of the popular low carbohydrate diets is that they draw attention to the quality of the carbohydrates that we’re eating. Most Americans are choosing lots of refined, sugary, calorie-rich (but nutrient-poor) carbohydrates like soda, candy, white bread products, white rice, and processed french fried…
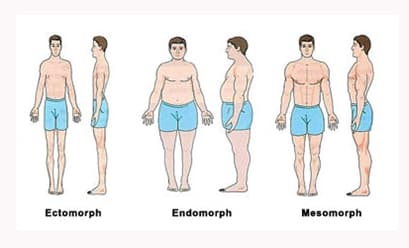
Men are subject to issues concerning body image as much as women. Currently, two competing body types dominate the pages of GQ and Men’s Health. The first is a slender, sculpted, almost feminine look (think Brad Pitt); the second is a pumped-up but still low-fat physique (think Nicolas Cage). Both images differ greatly from past…
Do you loathe and despise your body? Or maybe you wish if you could just change this one thing… Well, you’re not alone. Far from it. Whether you feel you are too fat, too skinny, too tall, too short, too hairy, not hairy enough, too-something — or just not something enough –- everyone feels like…
Attempting to enter the basic American search for self-control, individuality and thinness has not brought most people more health and happiness. Instead, we often feel as if we have failed and the blame is laid squarely on our shoulders. But the social requirement that we achieve the “ideal weight” is based on the presumption that…
Foodborne illness, often called ‘food poisoning’, occurs when a person gets sick by eating food that has been contaminated with bacteria, parasites or viruses, also known as ‘microbes’ and ‘pathogens’. Foodborne illness is the largest class of emerging infectious diseases. This is due to the changing population demographics, changing patterns of food production and consumption…
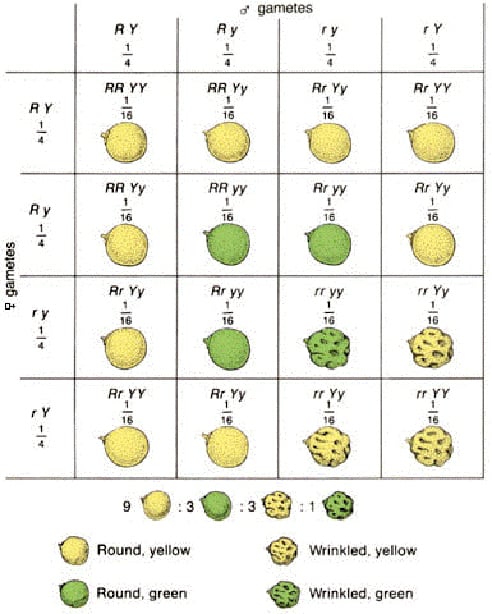
Dihybrid cross = involves inheritance of 2 characteristics Example 1: In Pisum sativum, a round seed is produced by a dominant allele (R), while wrinkled seeds are produced by the recessive allele (r). Yellow seeds are produced by the dominant allele (Y), while green seeds are produced by the recessive allele (y). In a cross…
The difference between an allergy and intolerance: Food Allergy Occurs when the immune system reacts to a certain food The body creates immunoglobin E (IgE) When these antibodies react with food the body releases massive amounts of chemicals and histamines to protect the body – causing a number of symptoms of an allergic reaction Food…
TECHNIQUE DEFINITION Bake To cook breads, cookies, veggies, casseroles and some meats in an oven. Beat To thoroughly mix ingredients by stirring rapidly in a circular or over and over motion. Blend To mix two or more ingredients together until combined. Also known as combining ingredients. Boil To cook food in a liquid that…
-From the start there exists a materialist connection of humans with one another, i.e., the satisfaction of basic needs. – The first historical act is the act of production of the means to satisfy these needs, the production of material life itself. -Humans work on nature and through that relation emerges a cultural system of…
First Amendment – Establishment Clause, Free Exercise Clause; freedom of speech, of the press, and of assembly; right to petition. Congress shall make no law respecting an establishment of religion, or prohibiting the free exercise thereof; or abridging the freedom of speech, or of the press; or the right of the people peaceably to assemble,…
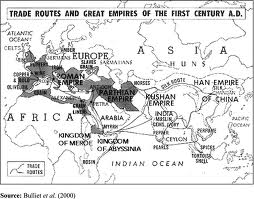
Route: Indian Ocean Advantages: Changeable, predictable monsoon wids lead to reliable schedules; great variety and amound of goods can be carried via ship (emporium trading); seaborne trade usually faster than land routes Geographical Scope: East Africa, Arabia, Inida, S.E. Asia; canal between Red Sea and Nile would eventually connect Mediterranean Commerce: Aromatic (incense), spices, gold,…
DEFINITION: Identifying Point of View (POV) is an attempt at establishing an author’s bias and/or motivation within a primary source. Clarifying an author’s logic in his/her opinions is a form of high level analysis. SOME METHODS OF IDENTIFYING POINT OF VIEW: Political ideology, Class, Race, Religion, Nationality, Profession, Gender POV is NOT: An author’s opinion.…
State Leader & Symbolic Role Method of Unification Ruler’s Means of Control Egypt Pharoh (herdsman) sometimes functions as god. Organizing labor to manage floods; distribution of food; use of Nile River as highway to unify, control. Pharaoh’s commands, policies function as law, regarded as devine. Mesopotamia city-states King/Royals, mediate, lead, worship, receive oracles. Organizing labor;…
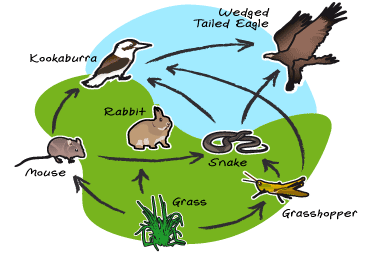
Niche An organism’s ecological ROLE in the environment (NOT HABITAT!) All components of lifestyle and how they affect other organisms Three Types of Symbiosis Mutualism both species benefit Commensalism one species benefits, the other is unaffected Parasitism one species benefits, the other is harmed Lichen Lichen is really two organisms: algae and fungus. The fungus…
Characteristics of Life Living things are organized. Living things are made up of cells. Living things metabolize. Living things maintain an internal environment. Living things grow. Living things respond. Living things reproduce. Living things evolve. Seven Levels of Taxonomic Classification Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Kingdom Animalia Characteristics All animals are multicellular, eukaryotic…
Mycology Myco- = fungus -ology= study of General Characteristics of Fungi: Eukaryotic Decomposers – the best recyclers around No chlorophyll – non-photosynthetic Most multicellular (hyphae) – some unicellular (yeast) Non-motile Cell walls made of chitin (kite-in) instead of cellulose like that of a plant Are more related to animals than the plant kingdom Lack true…
The largest animal phylum- 1 million species of crabs, shrimp, spiders, scorpions, and insects make up this phylum Have jointed appendages; segmented bodies Exoskeletons made of chitin Molt; have heads with many sensory organs. Bilateral Simple and complex eyes that detect only light intensity and form images Antennae that smell chemical substances in the environment…