William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
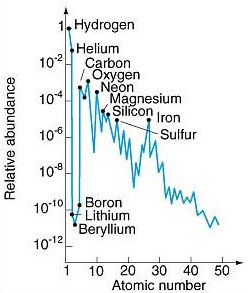
There are 92 naturally occurring elements; only 17 of them make up 99.5% of the earth’s crust (including oceans and atmosphere). In living things (plants, animals, people) the six most abundant elements are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sulfur. The universe is dominated by the elements hydrogen (83%) and helium (16%) 1. The Crust…
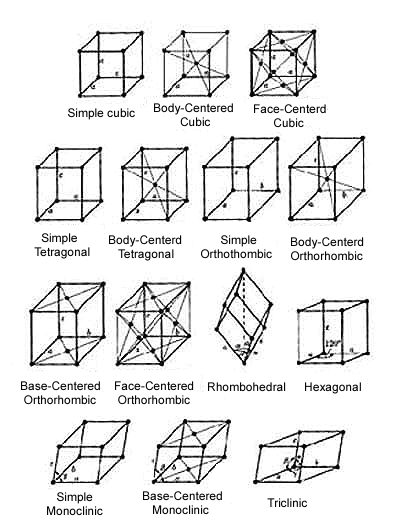
The study of the growth, shape, and geometric characteristics of crystals is called crystallography. When the conditions are right, each chemical element and compound can crystallize in a definite and characteristic form. Thirty-two classes of crystals are theoretically possible, almost all common minerals fall into one of about twelve classes, and some classes have never…
It is atomic number 81. It has 81 protons and electrons and 123 neutrons. Thallium has a mass of 204.3833 atomic mass units. Its symbol is Tl. It resides in Group IIIA of the periodic table. That is the aluminum family. Thallium has a bluish color after exposure to the air. It is a very…
Atomic Number: 43 Atomic Symbol: Tc Atomic Weight: (97) Electron Configuration: -18-13-2 Element 43 was predicted on the basis of the periodic table, and was erroneously reported as having been discovered in 1925, at which time it was named masurium. The element was actually discovered by Perrier and Segrein Italy in 1937. It was found…
Silicon is the raw material most often used in integrated circuit (IC) fabrication. It is the second most abundant substance on the earth. It is extracted from rocks and common beach sand and put through an exhaustive purification process. In this form, silicon is the purist industrial substance that man produces, with impurities comprising less…
Robert Boyle is considered both the founder of modern chemistry and the greatest English scientist to live during the first thirty years of the existence of the Royal Society. He was not only a chemist and a physicist as we know him to be, but also an avid theologian, a philanthropist, an essayist, and a…
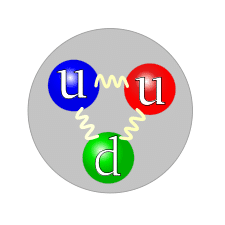
Quarks- any group of subatomic particles believed to be among the basic components if matter Quarks are believed to be the fundamental constituents of matter, and have no apparent structure. They are the particles that make up protons and neutrons, which make up the nucleus of atoms. Also, particles that interact by means of the…
Pyrite, also known as Fool’s Gold is the most common of the sulfide minerals. Pyrite is called Fool’s Gold because of it’s pale brass yellow color and glistening metallic luster, but it may be told from gold by it’s cubic, dodecahedral, and octahedral crystals and fine grain masses. Some interesting facts about pyrite are that…
Plutonium is a radioactive metallic element. Although it is occasionally found in nature, mostly all of our plutonium is produced artificially in a lab. The official chemical symbol for plutonium is Pu, coming from its first and third letters. Its atomic number is ninety-four. Plutonium is able to maintain its solid state until very high…
Historically, the term smog referred to a mixture of smoke and fog, hence the name smog. The industrial revolution has been the central cause for the increase in pollutants in the atmosphere over the last three centuries. Before 1950, the majority of this pollution was created from the burning of coal for energy generation, space…
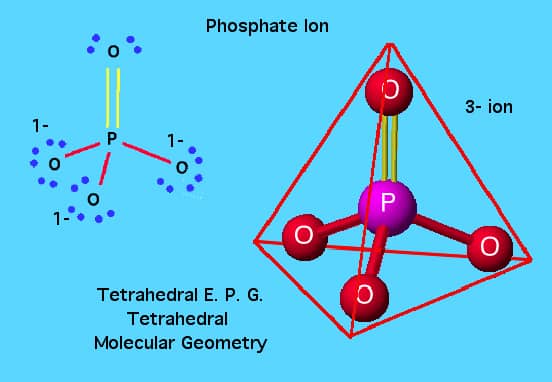
Phosphates may be created by substituting some or all of the hydrogen of a phosphoric acid by metals. Depending on the number of hydrogen atoms that are replaced, the resulting compound is described as a primary, secondary or tertiary phosphate. Primary and secondary phosphates contain hydrogen and are acid salts. Secondary and tertiary phosphates, with…
Pheromones{fair’-uh-mohn} (from the Greek pher, “to carry” and horman “to stimulate”) are chemicals released by organisms into the environment, where they serve as signals or messages to alter behavior in other organisms of the same species. Pheromones are a class of compounds that insects and animals produce to attract members of their own species. These…
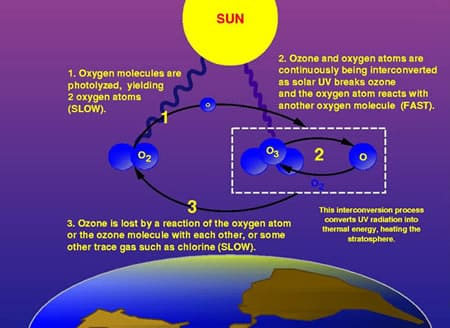
Triatomic oxygen, O3, is most commonly known as ozone. It has a resonance structure, and can be drawn in two different ways: O=O- O-O=O It is a bluish, explosive gas at room temperature, and has a boiling point of -119°C. It has a melting point of -193°C, and is a blue liquid. It’s critical temperature…
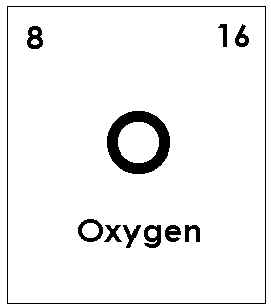
Oxygen and its compounds play a key role in many of the important processes of life and industry. Oxygen in the biosphere is essential in the processes of respiration and metabolism, the means by which animals derive the energy needed to sustain life. Furthermore, oxygen is the most abundant element at the surface of the…
Nobelium has the symbol No and is a radioactive metallic element with an atomic number of 102. Nobelium is in the actinide series being labeled as one of the transuranium elements. The element is named after Alfred Bernhard Nobel, the Swedish inventor and philanthropist. Nobelium can be found when produced artificially in a laboratory. Discovery…
In 1909 Robert Andrew Millikan set up an apparatus to measure the charge of an electron within an accuracy range of 3%. In 1913 he came out with a value of the electrical charge that would serve the world of science for a generation. Young Millikan had a childhood like most others: he had no…
Mercury is a metallic element that is a liquid at room temperature; it is one of the transition elements. Mercury’s atomic number is 80. It is superconductive when cooled to within a few degrees of absolute zero. Mercury was once known as liquid silver or quicksilver which was studied by the alchemists. Mercury was first…
On April 23, 1858 Max Karl Ernst Ludwig Planck was born in Kiel, Germany. He was the sixth child of a law professor at the University of Kiel. At the age of nine his interest in physics and mathematics was developed by his teacher Hermann Muller. When he graduated at the age of seventeen he…
LIFE OF MARIE CURIE Marie Curie(1867-1934) was a French physicist with many accomplishments in both physics and chemistry. Marie and her husband Pierre, who was also a French physicist, are both famous for their work in radioactivity. Marie Curie, originally named Marja Sklodowska, was born in Warsaw, Poland on Nov.7, 1867. Her first learning of…
Linus Carl Pauling was born in 1901 and died in 1994. He was an American chemist and physicist, whose investigations into the structure of molecules led to discoveries of how chemicals bond. Pauling was born in Portland, Oregon, on February 28, 1901, and educated at Oregon State College and the California Institute of Technology (Caltech).…