William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
The introduction of liberalism in the 18th century meant a new age in British politics, which continued through the Industrial Revolution Gladstone (Liberal) and Disraeli (Conservative) were two of the most influential political leaders of the late Industrial Revolution Both advocated reform of social structure; as a result, some of the more productive governments came…
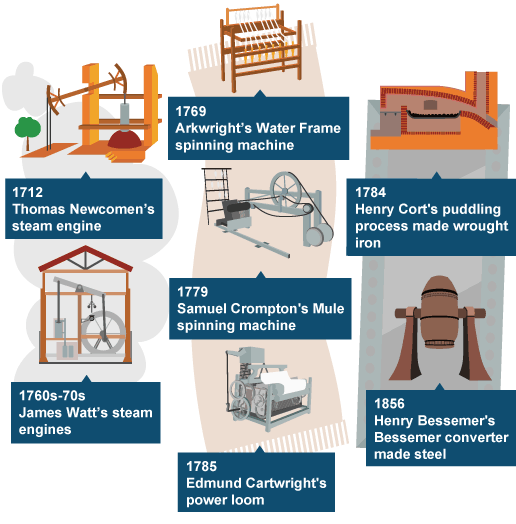
Industrial Revolution, a term usually applied to the social and economic changes that mark the transition from a stable agricultural and commercial society to a modern industrial society relying on complex machinery rather than tools. Dramatic changes in the social and economic structure took place as inventions and technological innovations created the factory system of…
POETRY A type of literature that expresses ideas, feelings, or tells a story in a specific form (usually using lines and stanzas) POET The poet is the author of the poem. SPEAKER The speaker of the poem is the “narrator” of the poem. POETRY FORM FORM – the appearance of the words on the page…
The Elements Include: Plot Symbolism Character Theme Setting Irony Point of View Tone and Style PLOT An author’s selection and arrangement of incidents in a story shape the action and give the story a particular focus. Discussions of the plot include not just what happens, but also how and why things happen the way they…
A literary essay analyzes literature A literary essay must be primarily analytical It doesn’t just say what happened (this is simply plot summary and belongs in a book report, not an essay) It doesn’t just say what the theme is but explains how the writer conveys the theme It doesn’t just give examples of something…
Written by William Shakespeare in 1605 Macbeth is a man who overthrows the rightful King of Scotland Shakespeare wrote Macbeth at the beginning of King James I reign Before James succeeded Elizabeth I he was king of Scotland Placing the play in James’ homeland probably pleased him Will the real Macbeth please stand up? Macbeth…
The earth, its relation to the stars and planets, and speculations as to its origin attracted human curiosity long before the birth of the geological sciences. Although such studies fall more properly within the realm of astronomy,’ a brief survey of the earth and its planetary relations will provide the reader with some understanding of…
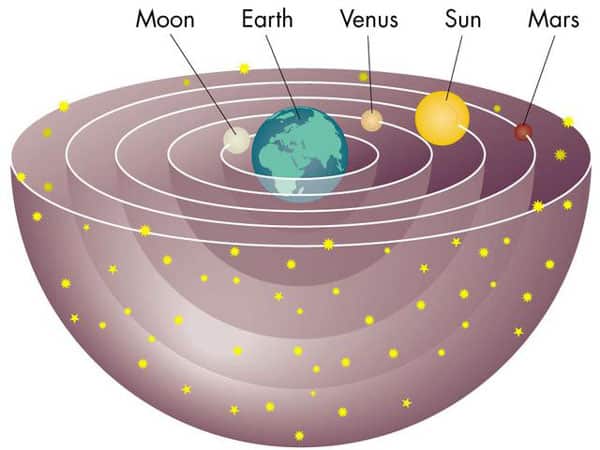
The earth is but one of nine planets which make up our solar system. But to humans Earth is by far the most important of all planets, for it is our home. It is also, so far as we know, the only planet which supports any type of life. Whence came the earth? How and…
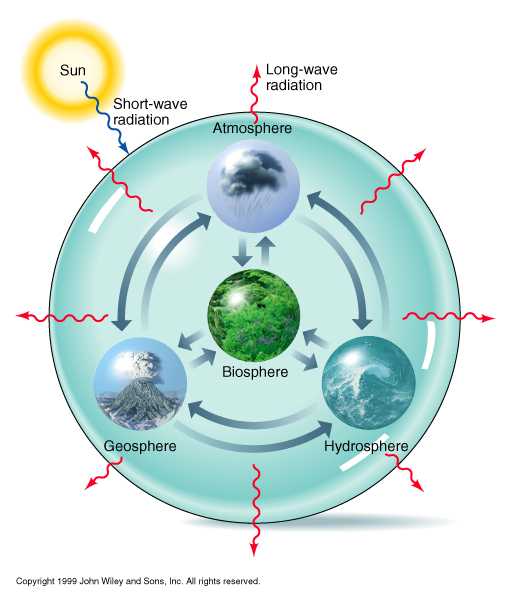
The earth consists of air, water, and land. We recognize these more technically as the atmosphere, a gaseous envelope surrounding the earth; the hydrosphere, the waters filling the depressions and covering almost 71 percent of the earth; and the lithosphere, the solid part of the earth which underlies the atmosphere and hydrosphere. The Atmosphere. The…
THE LITHOSPHERE The part of the earth that is made up of rocks and minerals, consists of the uppermost layers of the earth Came into being billions of years ago and still continues to change and evolve Changes to the worlds land masses, tectonic plates Volcanoes, earthquakes THE HYDROSPHERE The part of the earth made…
What is light? A form of energy that the Sun emits in all directions Properties of Light Light travels in straight lines: Light travels VERY FAST – around 300,000, 000 metres per second. (3.0 x 108 m/s) Light travels much faster than sound. For example: Light energy is transferred through radiation RADIATION A method of…
Geocentric view: Earth-centered view. (600BC – 150 AD) Came from the belief that God created humans at center and everything moved in perfect divine circles. Earth was a sphere that remained motionless at center of the universe Sun, Moon, Mercury, Venus, Mars, Jupiter and Saturn orbited earth in circles Stars traveled around the earth on…
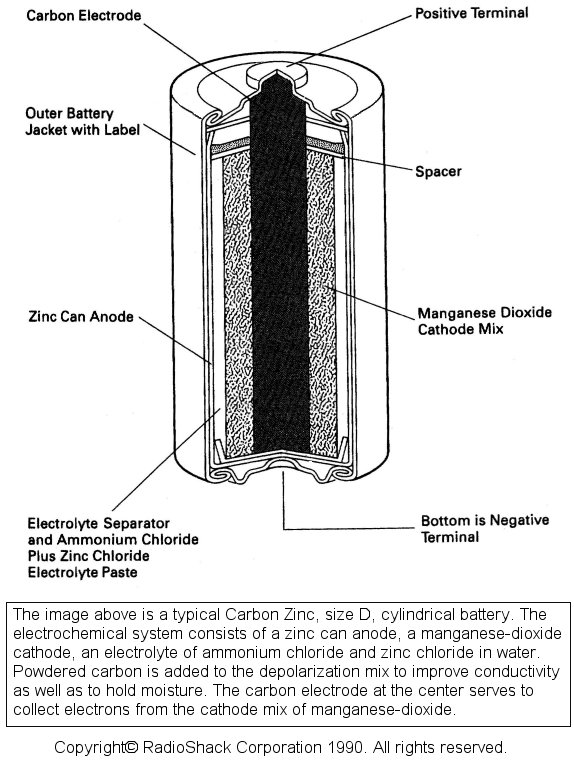
A material that lets electrons flow through it is called a CONDUCTOR The molecules of all types of conductors resist the flow of electrons to some degree ELECTRICAL RESISTANCE is a measure of how easy or hard it is for electric current to move through a material Conductors have low resistance Insulators have high resistance…
Energy can be defined as the ability to do work. Electrons possess energy and this energy can be converted to another form to do work (make a lightbulb shine, motor run, etc). This energy is called electric potential energy. Definitions: Electric potential energy: energy that the battery gives to the electrons; the amount of energy…
There are four major types of industry in Canada/USA/Europe. Primary, Secondary, Tertiary and Quaternary. Primary Industries Industries that take in raw materials from the natural environment. Also known as extractive industries. (known as primary because extraction or removal of natural resources must happen before anything else can be made. Everything comes from the earth) Primary…
80 % of Canadians live in cities cities are broken up into 6 major land-use groups – residential, transportation, institutional and public buildings, open space and recreational land, industrial, and commercial Residential Land Use Where people live includes low (houses), medium (town houses) and high density (apartment buildings) Takes up 40% of land in cities…
The Norse had explored and wintered in North America some 500 years before Giovanni Caboto, a Genoese explorer whom the British called John Cabot, rediscovered the land in 1497. Although Cabot failed to find a northern route to the rich spice trade in Asia, he returned with tales of an ocean teeming with cod and…
Population distribution – the pattern of where people live in a region, or across the country. There are 2 main patterns, dispersed and concentrated Two main catgories of settlement in Canada. Rural ,and Urban Rural – outside of cities and towns, low population density, dispersed settlement pattern Three factors affect pattern of rural settlement 1.…
FOUR MAIN PARTS TO SOIL 1. Minerals – comes from the weathering (chemical, physical) of the parent material. The inorganic material in soil is made up of rock material mainly. It can be sand, silt or clay. The particles in each of these rock types are ordered from larger to smaller with sand being the…
Layers of rocks can be faulted, folded and tilted by large forces within the Earth’s crust. The study of these changes can give information about the strength and direction of the forces involved. Sedimentary rocks – layers of rock fragments that were compressed and cemented together. They often contain fossils. Igneous rocks – molten rock…