William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
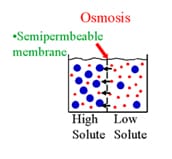
Biological Solutions Solutes are substances that are dissolved in a liquid to form a solution. The liquid that the solutes are dissolved in is referred to as a solvent. In biological systems, molecules that must enter or leave cells are the solutes and water is the solvent. Diffusion All particles are constantly and randomly moving. …
Components: i) plasma ii) erythrocytes (red blood cells) iii) leukocytes (white blood cells) iv) platelets Plasma: o 55% of blood volume and is 90% water o Contains dissolved materials which are being transported: o proteins (fibrinogen), hormones, nutrients, waste products, gases Erythrocytes: o Function: > to carry oxygen o Structure: > no nucleus, cytoplasm contains…
The atom is the basic unit of matter. Atoms bond to one another to form compounds. Bonds are formed by the sharing or transfer of electrons present in the atoms. Bonds between Atoms: Chemical Bonds Covalent compounds – formed by the EQUAL sharing of electrons between atoms – electrically neutral molecules (no “+” or “-“…
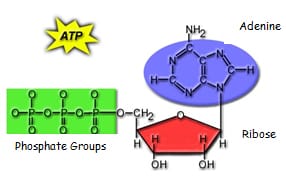
Energy – needed for: – movement – synthesis of complex compounds – active transport Food – provides energy needed by cells – broken down > heat (body heat, excess removed) chemical storage form Cellular Respiration – is the process by which chemical energy stored in food (usually glucose, but may be protein and lipids is…
Cells must perform thousands of different chemical reactions in order to survive. These reactions are crucial to providing cells with energy. Endergonic reactions: -“energy in” require energy in order to proceed – biological endergonic reactions produce molecules that store energy (ex. Glucose) – Ex. Photosynthesis Exergonic reatctions: – “energy out” release energy – biological exergonic…
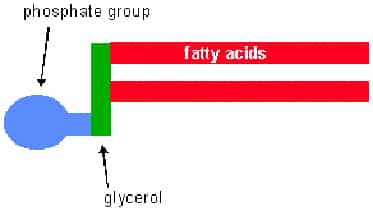
The plasma membrane surrounds the cell and is crucial to cell life: it must control what enters and leaves the cell. It must allow sufficient amounts of food molecules, such as glucose, to pass into the cell and must also allow for the quick removal of waste products from the cell. Membrane Structure Phospholipids Most…
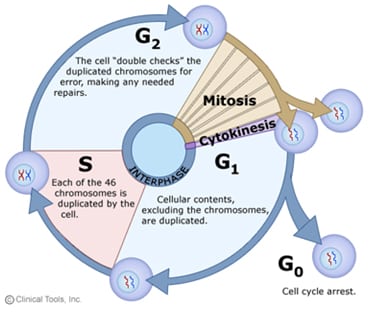
Genetic continuity is the transmission of hereditary material through cell division. The Cell Cycle – cells do not divide continuously– in cells capable of dividing, the period between cell divisions is called interphase– cells spend most of their time in interphase because this is the phase where they perform their functions (obtaining energy, synthesizing products,…
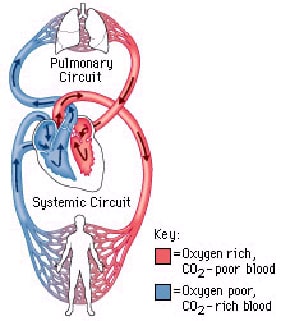
Functions: 1. transport oxygen and carbon dioxide 2. distribute nutrients and transport of wastes 3. maintenance of body temperatures 4. circulation of hormones Structure: Made up of three components: 1. A fluid in which materials are transported (blood) 2. vessels in which the fluid moves (blood vessels) 3. a pump (the heart) Circulatory system is…
Observations of chemical reactions are summarized in certain generalizations called the laws of chemical change. The three laws of chemical change are; 1) Law of Conservation of Mass 2) Law of Constant Composition 3) Law of Multiple Proportions Law of Conservation of Mass States that during a chemical reaction, matter is neither created or destroyed…
Plot and Sequence Fiction includes novels, short stories and other writings that tell about imaginary people and events. The plan or main story in a piece of fiction is called the plot. Understanding the order of events in a plot is important when you are reading. You probably expect the narrator, or storyteller, to start…
Character Getting to know the characters in a story is like becoming acquainted with a person you have just met. It takes a little more time to learn what the person is like. You learn from what others say about the person. Motivations Motivations are the reasons characters behave the way they do. Notice what…
The setting of a story is the time and place in which the events occur. Think of a movie or TV show that you have watched recently. Was the story about people today or about people from the past or future? How did you recognize the time period? Did the characters’ clothing, hairstyles, and speech…
Voice: is the manner in which a story is told so as to connect to readers on an emotional level or the author’s point of view. For example, the author speaks directly in his or her own person or a role or speaks through a persona. Audience: the people for whom the audience is written.…
From the stories you have read so far, it is clear that for a plot to exist, it must have characters, or people created by the author. Although these people are fictional, they must be believable and arouse your sympathy or interest if the story is to hold your attention. Every author, in his own…
Imagery is the use of descriptive language to create an image in the minds of the readers. Shakespeare uses many kinds of images in his play. Here are 4 kinds of imagery we find frequently in Romeo and Juliet: Metaphor: describing something by comparing it to something else without the use of “like” or “as”…
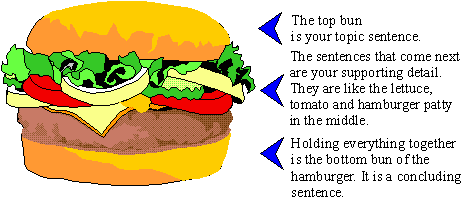
A paragraph is a unit of writing that consists of one or more sentences focusing on a single idea or topic. A well-written paragraph often has the following structure: Topic Sentence: This sentence outlines the main idea that will be presented in the paragraph. Support Details or Examples: This is the part of the paragraph…
Cost-plus Pricing – A markup is added to the cost price to ensure a profit Markup = selling price – cost price Markup % = selling price – (cost price/cost) X 100 Follow-the-competition Pricing – The price of the product or service is set equal to or slightly below a competitor’s price. The pricing can…
BRANDING AND POSITIONING PACKAGING Who packages the items? Raw material processors, manufacturers, retailers Why and how are things packaged? Protection Convenience Information Environmentally Friendly Promotion Appearance and Branding Packaging is often referred to as “THE SILENT SALESPERSON” 6 FUNCTIONS OF PACKAGING Protection Protect from breakage (bubble wrap, foam) Protect from germs, air, sunlight, dust/dirt (air…
Cultural anthropology is the study of how culture shapes human ideas and learned behaviours. It examines how cultures have developed and compares similarities and differences among them. Cultural anthropologists base their knowledge on observation. They try to be objective and draw conclusions from data, without imposing their own personal judgments. Many times anthropologists are faced…
Anthropology: The study of the lives and cultures of humans alive or dead. Anthropologists: Use reason to gain knowledge and insight into human kind Examine how humans live, think, communicate, produce and interact with their social and physical environment Study how different people can be and how much different people have in common Physical Anthropology:…