William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
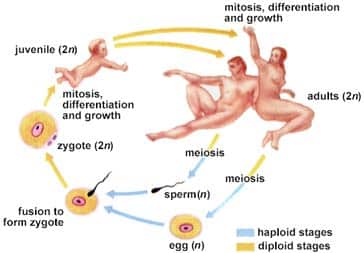
Sexual reproduction: production of offspring; union of male and female gametes Gametes: eggs and sperms cells in animals Sexual reproduction depends on Meiosis; specialized process of cell division; recombines DNA sequences, produces cells with half the number of chromosomes in somatic cells. (chromosome= reduction) Fertilization: nuclei of egg/ sperm fuse; producing zygote (# chromosomes typical…
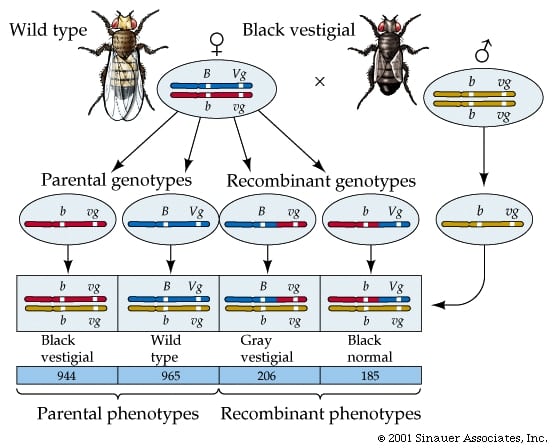
Genetic linkage: genes located on the same chromosome may be inherited together in genetic crosses. Linked Genes: Genes on the same chromosomes Morgan- first to map genes; can’t directly measure the distance between genes Do it indirectly- genes sitting far apart on a chromosome would be more likely to be separated from one another during…
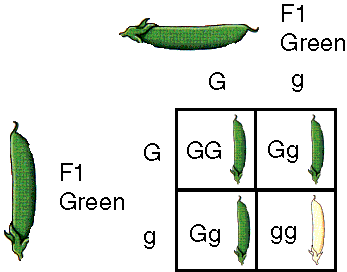
Blending theory of inheritance: hereditary trait blend evenly in offspring through mixing of parent’s blood. Mendel studied heritable characteristics called characters; plant color and seed shape. Variation in character= Trait Monohybrid cross between to heterozygous parents (Dr x Dr) F1 generation will yield phenotypic ration of 3:1 (1/4 getting PP or pp, or ½ getting…
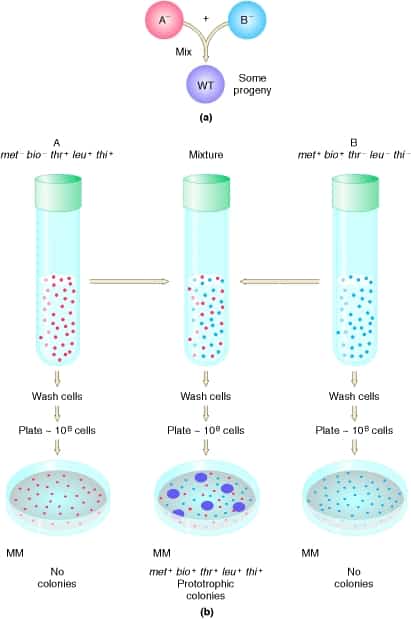
Genetic recombination needs: Homologous chromosomes; must differ from one another along one at least two spots Mechanism to bring into close proximity of each other Homology allows the DNA to line and recombine precisely. Cut and passing 4 DNA backbones results in 1 recombination event. Lederberg Experiment E.coli grown in minimal medium; contains water, organic…
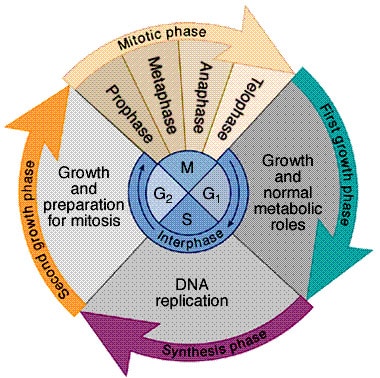
Cell Cycle: nuclear division, cytokinesis Parental cell: genetic copies of parental cell 3 process: checks/ regulators for each step to ensure timely progression, replication process to synthesis DNA into two copies, interwoven “cables” and “motors” of mitotic cytoskeletons. Chromosomes: nuclear units of genetic information; DNA molecules combined with proteins. In eukaryotes, heredity information of nucleus…
Sexual response cycle – four stage cycle experienced during sexual arousal Excitement phase – arousal builds rapidly Plateau phase – respiration, heart rate, vasocongestion, and muscle tension continue to build until there is enough muscle tension to trigger orgasm Orgasm phase – males: rhythmic contractions of internal organs and muscle tissue surrounding the urethra project…
Motivation – process that influences the direction, persistence, and vigour of goal directed behaviour Perspectives on Motivation Instinct Theory and Modern Evolutionary Psychology Instinct (fixed action pattern) – an inherited characteristic, common to all members of a species, that automatically produces a particular response when the organism is exposed to a particular stimulus Theories faded…
Metabolism – body’s rate of energy utilization Two-thirds of energy used goes to support basal metabolism, the resting, continuous metabolic work of body cells Immediate energy supply information interacts with other signals to regulate food intake (hunger not necessarily linked to immediate energy needs) Homeostatic mechanisms are designed to prevent people from running low on…
Two types of reasoning: Deductive reasoning – reasoning from a general principle to a specific case Basis of formal mathematics and logic Viewed as stronger and more valid reasoning because conclusion cannot be false if premises are true Syllogism: If all humans are mortal (first premise), and Socrates is a human (second premise), then Socrates…
Language: History and Structure Language – a system of symbols and rules for combining these symbols in ways that can produce an almost infinite number of possible messages and meanings Three critical properties of language: Symbolic: Uses sounds, written signs, or gestures to refer to objects, events, ideas, and feelings Displacement – capacity of language…
Memory – processes that allow us to record and later retrieve experiences and information Memory as Information Processing Encoding – getting information into the system by translating into a neural code that your brain processes Storage – retaining information over time Retrieval – the process of accessing information in long term memory Three-Component Model Three…
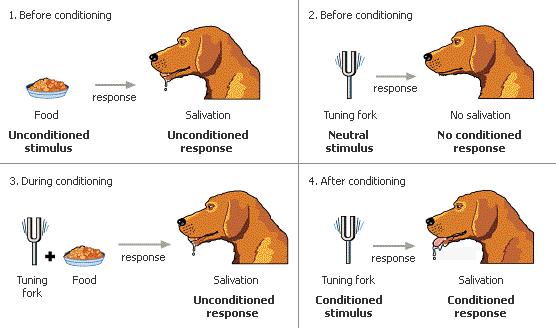
Learning – process by which experience produces a relatively enduring change in an organism’s behaviour or capabilities Adapting to the Environment Behaviourists focus on how organisms learn, examining the processes by which the experience influences behaviour Ethology focuses on the functions of behaviour Adaptive significance – how behaviour influences an organism’s chances for survival Fixed…
Consciousness – our moment to moment awareness of ourselves and our environment Has various characteristics: Subjective and Private – reality and experience depend on the individual Dynamic – consciousness experiences are ever-changing and a continuous flow of mental activity Self-reflective and Central to Our Sense of Self – mind is aware of its own consciousness…
Sensation – the stimulus-detection process by which our sense organs respond to and translate environmental stimuli into nerve impulses that are sent to the brain Perception – active process of organizing the stimulus input and giving it meaning Sensory Processes Stimulus detection – absolute threshold designated as the lowest intensity at which a stimulus can…
Psychology = The scientific study of behaviour and the factors that influence it. Taking into account Biological, Individual and Environmental factors. Basic and Applied Science Two types of research: Basic research: Knowledge gained purely for its own sake. The goals are to describe how people behave and to identify factors that influence it. Research maybe…
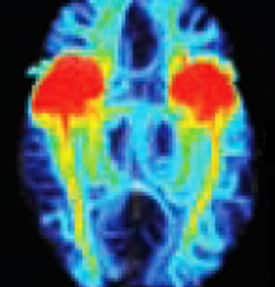
Scores on neuropsychological tests show amount of damage done to person Destruction and Stimulation test: can destroy parts of the brain to see effect or stimulate nerves with electrodes (Dr. Penfield- famous neuroscientists) – mapped motor and sensory areas Broca’s aphasia: could understand, but not speak Dorsal Stream: action (D.A) Ventral Stream: perception (V.P) Single-…
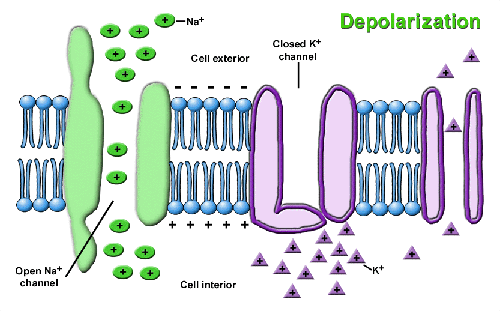
Neurons: constructive unit of the nervous system; interconnected like electrical circuits Made up of: Soma (cell body): contains nucleus, keeps nerve cells alive (grey matter) Dendrites: receiving portion of nerve cell- receiving end of cell Axon: sends impulses away from the cell (white matter) Dendrites and axons are all interconnected; vary in shape and size…
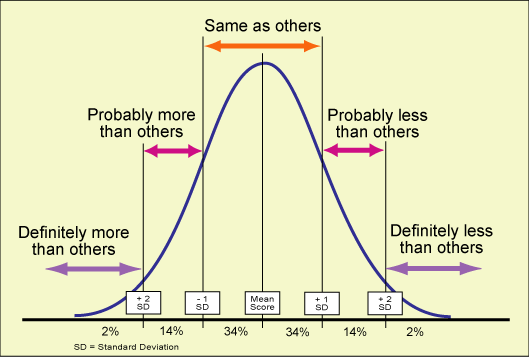
Descriptive Statistics: Summarizes and describes characteristics of a set of scores for a group Frequency Distribution: # of people who received each score Histogram: frequency distribution turned into a graph. The measure of central tendency: mean (average), median (middle), mode (most often) The measure of variability: provide info about the spread of scores (i.e range)…
Key scientific attitudes: Curiosity, skepticism, open-mindedness Hindsight: explaining behavior after the fact (problem: multiple conflicting outcomes and explanations for results) Use Scientific Process with variables and factual observations Scientific Process: Formulate a question based on observed events Formulate a tentative explanation for why those event transpired (hypothesis) Conduct research to test it Analyze research and…
What is a summary? A summary paragraph re-states the main idea of the text A summary is usually 1/3 length of original text A summary is written in your own words A summary is written in 3rd person (no I, me, you…) A summary is NOT: Written in 1st person Your opinion on the topic…