William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
Location Location is the arrangement and presentation of physical and temporal elements in a work. Time time of year (season) time of day (morning, afternoon, evening) month (September, January) era, century, decade (Victorian, 20th century, 1920’s) duration of the narrative details of the passage of time (falling leaves – autumn, snow – winter) sequencing of…
Rhetoric essentially means the art of speaking persuasively. It is the use of language in a formalized way in order to convince or have an effect on an audience. A) Word order Manipulation of common word order to create an effect B) Word choice Figurative language (oxymoron, onomatopoeia, assonance, alliteration, hyperbole, understatement, irony, allusion, litotes,…
PERSONAL CHARACTERISTICS OF THE ENTREPRENEUR (RISK TAKER, GO GETTER ETC.) UNWILLINGNESS TO DEVOTE THE IMMENSE AMOUNT OF TIME AND EFFORT REQUIRED TO MAINTAIN THE BUSINESS. THEY MAY HAVE TO LITTLE KNOWLEDGE OF THE BUSINESS AND HOW TO RUN IT. FAILURE TO DEVISE AN ADEQUATE FINANCIAL PLAN FOR THE BUSINESS AND TO ASSESS ITS ABILITY TO…
SUBSTANTIVE LAW: Consists of laws that list the rights and obligations of each person in society. PROCEDURAL LAW: Is the process of the law; outlines the steps in involved in protecting the rights given under substantive law. PUBLIC LAW: Controls the relationship between the governments and the people who live in society. Main types: criminal,…
Canadian Parliamentary System Federal Level Provincial Level Constitutional Monarchy A government in which the monarch has only the powers laid out in the nation’s constitution and laws. The monarch is recognized as the Head of State and centre of state authority. Role is essentially symbolic; most real political power in Canada lies with elected politicians.…
What is Propaganda? Propaganda is a specific type of message presentation aimed at serving an agenda. The purpose of propaganda is ‘to spread a philosophy or point of view’. The most common use of the term (historically) is in political contexts; in particular to refer to certain efforts sponsored by governments or political groups. Each…
Militarism Alliances Imperialism Nationalism Militarism Def: Building up of arms (weapons) to deter (scare) others from attacking. Germany was competing with the UK to build battleships. The British feared an attack on their Empire Germany was competing with Russia and France to expand their armies Alliances Def: Banding together of countries against a common threat.…
Confederation Day July 1, 1867 – Canada first became a nation – BNA Act 4 British colonies joined to form the new Dominion of Canada Ontario, Quebec, Nova Scotia & New Brunswick (population = 3 million) John A. McDonald sworn in as Canada’s first prime minister The Twentieth Century (1900-1913) Some colonies rejected confederation – …
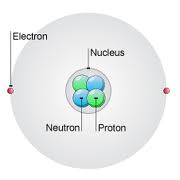
Isotopes have the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons. This means that while the atomic number of an element will NEVER change…The MASS of the atom can change quite a bit depending on how many neutrons there are The number of protons in an atom is also called the “atomic number”. This…
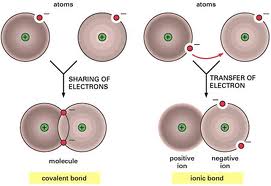
After reviewing the Bohr-Rutherford diagram you should know that atoms wish to “fill” electron orbits. Atoms tend to combine in a way that allows the resultant compound to be neutral but have only full electron orbits on the atoms. Lets do an example: Note: I draw the electrons with holes in noticeable places. In reality…
Latitude o imaginary lines that measure the distance north or south of the Equator (0°) o lines are parallel to the Equator at regular intervals (approximately 113 kilometres apart) What is Latitude? Its reference point is the equator. The equator’s latitude is O degrees. Even though the lines run horizontally, latitude measures north and south.…
Minerals are non-renewable resources found all over the world The Canadian Shield is the source of many of our mineral deposits Minerals can be divided into three groups: Metallic (copper, nickel, uranium, gold, etc) Fossil Fuels (coal, oil, natural gas) Industrial (stone, diamonds, salt, potash) Environmental Issues Mining can cause air pollution, acid precipitation, and…
Softwood Forests: coniferous trees (cone-bearing: fir, pine, spruce) make up 66% of Canada’s forests Hardwood Forests: deciduous trees (lose leaves every year: birch, maple) make up 12% of Canada’s forests Commercial Forests Trees are harvested to make a profit exists in warmer, wetter areas where trees grow quickly British Columbia, Alberta Non-commercial Forests Not profitable…
There are five major agricultural production sectors in Canada. They are….. grains & oilseeds (wheat, oats, rye, flax seed, canola, soybeans, and corn ) 34% red meats (beef, hog, veal, lamb) 27% dairy 12 % horticulture 9% poultry and eggs 8% Horticulture, poultry & eggs, and dairy are all produced with a domestic orientation –…
Key Terms Aboriginal Peoples: Descendents of Canada’s original inhabitants Treaty: An official agreement between the federal government and the First Nations – Aboriginal people give up their land rights (except for reserves) and accept treaty money/government assistance Reserve: Area of land set aside for status Indians Assimilate: To lose your culture and adopt the culture…
The statues ‘talk’ to you Life size renditions in bronze A whole room “frieze”- small tiles used to decorate the room and tell a story Dig for a subway- and find a village- with an intact water system (4000 year old) Keats’ Message “What leaf – fring’d legend haunt about thy shape Of deities or…
Themes: loneliness, indecision, and love. Prufrock is a man whose anxieties have isolated him. He doesn’t make decisions because he fears that they will turn out wrong He talks about love and about women Voice: J. Alfred Prufrock is speaking the poem (persona) Tone: it does change throughout the poem because at one point, he…
If good is to be rewarded and evil is to be punished, how do we define good and evil? Should we be obeying the law no matter what the content? What if the law itself is evil? The philosophers we will be looking at are a few of the influential thinkers of their day. Ancient,…
It has been argued that Adam Smith articulated two essential attributes in the economic system that was not yet fully born in his time: 1. A society of competitive profit-seeking individuals can assure its orderly material provisioning through the self-regulating market system. 2. Such a society tends to accumulate capital, and in doing so enhances…
Malthus based his ideas about population and food on two basic premises. 1) Food is necessary to sustain life 2) Human sexual instinct is constant. Starting with these two premises, Malthus built an argument that the population if unchecked would double every 25 years (about one generation) Population would progress geometrically Food production would be…