William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
Alan Austen, as nervous as a kitten, went up certain dark and creaky stairs in the neighborhood of Pell Street, and peered about for a long time on the dime landing before he found the name he wanted written obscurely on one of the doors. He pushed open this door, as he had been told…
Entropy, S, is the tendency towards randomness or disorder in a system – an ordered arrangement of particles has a lower entropy/disorder than the same number of particles in random arrangements Entropy becomes more disordered with: 1.) ^ Temperature – more chaotic motion 2.) ^ Volume of gases 3.) change in phys. State A change…
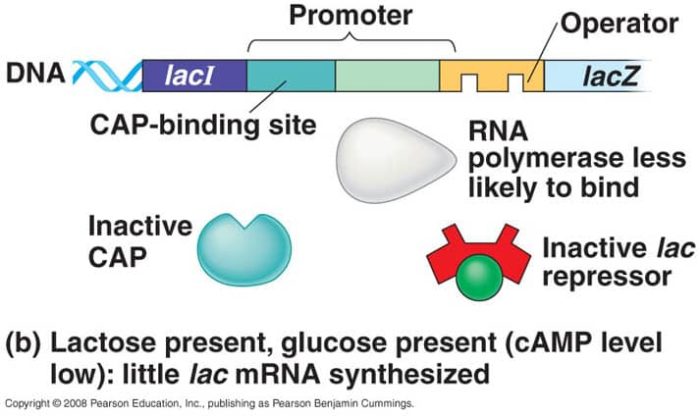
lac Operon Model Regulates production of enzyme B-galactosidase which is needed to break down lactose. It consists of a cluster of 3 genes under the control of one promoter and one operator. When lactose levels are low the LacI repressor protein binds to lac operator, covering part of the promoter region which blocks transcription of…
Protected groups have the explicit right to freedom from harassment in housing accommodation and employment. The Code defines harassment as “engaging in a course of vexatious [annoying or provoking] comment or conduct which is known or ought reasonably to be known to be unwelcome.” The most important word in the definition is “unwelcome.” We do…
Customs, rules, and agreements that govern relations between sovereign states. More recently also includes handling such matters as human rights within the borders of sovereign nations. Is international law real law? Domestic Law Vs. International law No international legislature passing laws – UN closest to such a forum No comprehensive judicial system – International Court…
1948 UN General Assembly adopted the Universal Declaration of Human Rights. Outlines basic human rights including: The right to life, liberty and nationality Freedom of opinion, conscience, and religion Right to work Right to an education Right to take part in the nation’s public business 1966 United Nations Convention on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights…
Direct Evidence: the testimony of witnesses who actually saw the offence being committed Circumstantial Evidence: indirect evidence; indicates that it is highly probable that the accused is the only one who could have committed the crime Similar Fact Evidence: shows that the accused has committed similar offences in the past Hearsay Evidence: something that someone…
Trial by Wager Required the accused to have a number of acquaintances (oath-helpers) swear his/ her innocence Not applicable to people caught in the act or with stolen property. They faced one of the following: Trial by Battle Evolved from Anglo-Saxon practice of “blood feud” where relative of victim tool revenge by attacking killer and…
Legal Defenses • Insanity • Automatism • Intoxication • Duress • Self-Defense • Alibi • Necessity • Mistake of Fact • Provocation • Officially induced error • Entrapment • Double Jeopardy Insanity • Accused cannot perform the Mens Rea of the offence or is not fit to stand trial. To Prove Insanity you must: • …
Aboriginal Rights: Collective rights rooted in historic cultural traditions and practices, based on ancestral use of the land. Rights as distinct peoples recognized in law and treaties Collective Rights: Rights held through membership to a group. All members have same rights. Areas of Concern: Self-government Land ownership Control of natural resources The Royal Proclamation, 1763…
SIGNIFICANT PERSON OR CONCEPT DEFINITION, OR IMPORTANCE TWO EXAMPLES HAMMURABI (POSITIVE LAW AS MADE BY A PERSON) Codification Retribution (eye for an eye) Patriarchal All Babylonians Subject to the law King is above the law Very harsh and cruel Son gets hand cut off if strikes father, not mother Doctor gets hand cut off if…
The most basic and important ideal of our legal system is justice. There are two dimensions of justice. These are formal justice and substantive justice. Formal Justice: Requires decisions be made in a non-arbitrary and consistent manner Established legal rules must be followed No person shall be regarded to be above the law Every person…
Schedule B, Part I of the Constitution Act, 1982, comprises the Charter. Section 52: the Charter is a part of the Constitution which is the supreme law of Canada and all laws must comply with it. Charter can only be altered through the amending formula – substantial consensus of all the provinces and the federal…
An academic thinker named Edward Fenton came up with the acronym PERSIAT. He wanted to find a way to structure intellectual analysis so that concepts and subconcepts could be quickly and properly classified. In the last few years, Fenton’s original concept has been expanded upon and the idea of Geographical analysis has been added. Currently,…
At the time when your Majesty resolved to admit me both to your council and to an important place in your confidence for the direction of your affairs, I may say that the Huguenots shared the state with you; that the nobles conducted themselves as if they were not your subjects, and the most powerful…
The laboratory is a safe place to experiment if you are careful and familiar with all the equipment. You must assume responsibility for the safety of yourself and your neighbours. This paper outlines the steps to use for safety and first aid in this classroom. Student bags or backpacks and coats are not permitted in…
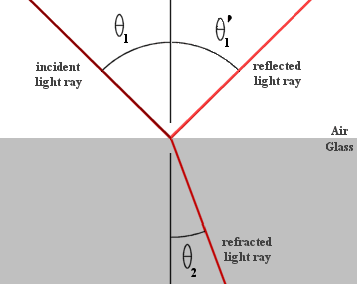
Indices of Refraction for Various Media: Medium Index of Refraction (n) Air/vacuum 1.00 Ice 1.31 Water 1.33 Ethyl alcohol 1.36 Vegetable oil 1.47 Acrylic 1.49 Glass 1.52 Diamond 2.42 1. Using Snell’s law, determine the constant when the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction are: a) 50˚ and 30˚ b) 30˚ and 18˚ …
Post World War II was a time of incredible political change in Canada MacKenzie King In 1945, the C.C.F. was becoming popular. King, the P.M. and leader of the Liberal party, wanted to find a way to “steal their thunder” and strengthen his party’s hold on Canadian politics. He introduced unemployment insurance to give unemployed…
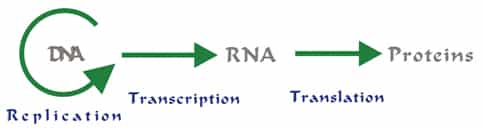
Nucleic acids are the storage form of all the genetic information required by a cell. They also are the cell’s preferred energy molecule ATP as well as acting as being used as intermediate electron carrier molecules in cellular respiration in the form of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and FAD (flavin adenine dinucleotide). cAMP (cyclic adenosine…
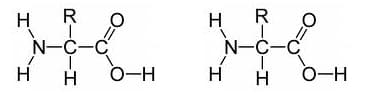
Proteins in the human body have a wide range of functions which include: Hormones (insulin, testosterone), Muscle Fibers (actin, muasin), Carrier Protein (Oxygen carrying hemoglobin), Structure/ Support (nails/ hair), Enzymes (biological catalyst), Membrane Transport (Na/ K pump), Cell-to-Cell Recognition, Antibodies. Structure Proteins are polymers made up of amino acid subunits bonded together by peptide bonds.…