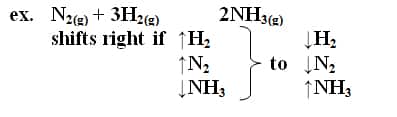William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
radiation = substance emits radioactive particles or waves Types of Radiation: 1) Alpha (a) particle – high energy helium nucleus 42He 2) Beta (b) particle – high energy electron no > p+ + e– 3) Gamma (g) waves – electromagnetic photons Natural Transmutations Radioactive decay = change in nucleus that produces radiation Transmutation = change…
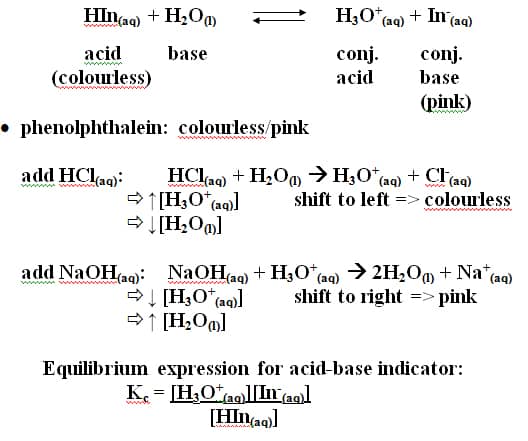
an indicator is an acid or a base that has a different colour from that of its conjugate general reaction for an acid indicator at equilibrium in an aqueous solution:
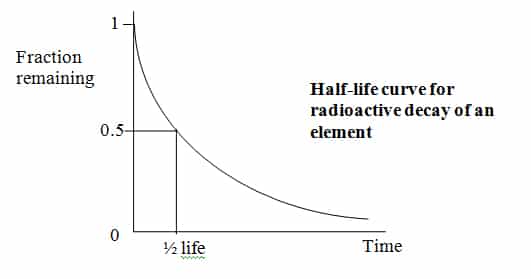
Period after which only half of the original number of nuclei in a sample of a radioactive element have not decayed. ex. half-life for uranium – 238 23892U = 4.6 x 109 years So after 4.6 x 109 years, only one half of the original uranium will be left
If an equilibrium in a system is upset, the system will tend to react in a direction that will re-establish equilibrium 1) Adding or Removing a Reactant or Product – reaction shifts in a direction that will remove a substance added or replace a substance removed 2) Changes of Temperature – increasing temperature shifts a…
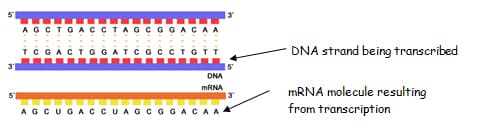
DNA: DNA is the genetic information or blueprint of who and what we are, and how we operate. This genetic information is devoted to the synthesis of proteins, which are essential to our body. Proteins are created from templates of information called genes in our DNA. The Code: – DNA molecules are long polymers of…
If I handed you a black guinea pig & asked, “What’s its phenotype for fur color?” You would gently hold the guinea pig, look at it and reply, “Black, you dummy … all you gotta do is look at it”. And I would say, “Correct, & please don’t call me dummy”. If I handed you…
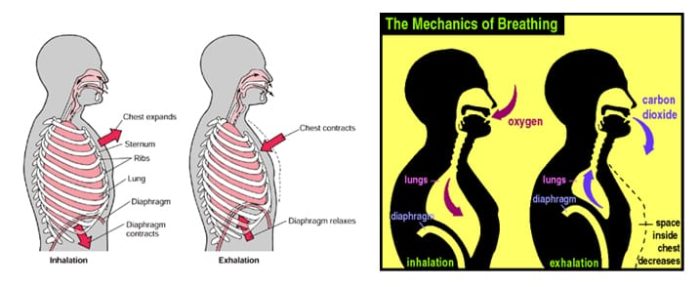
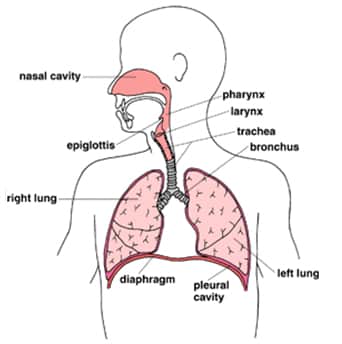
Efficient gas exchange can only occur if the alveoli are regularly flushed with fresh air. Diaphragm: a muscle connected to the bottom of the lungs Pleura: a membrane that connects the lungs to the walls of the chest cavity INHALATION: Mechanism > external intercostals plus the diaphragm contract to bring about inspiration intercostals elevate ribs…
Function supplies oxygen to cells and removes carbon dioxide defending the body against invasion of microorganisms control the body’s blood pH Components: Ventilation (breathing) > inhalation and exhalation; take in oxygen and dispose of carbon dioxide External Respiration > the exchange of gases between the alveoli and the blood Internal Respiration > exchange of gases…
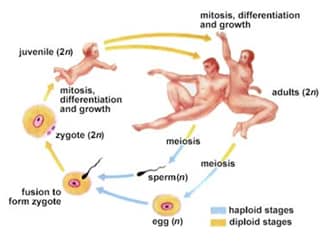
Sexually reproducing organisms create new offspring with the fusion of two parental cells. If two somatic cells, with a full complement of chromosomes, were allowed to unite, each new cell would have twice the number of chromosomes its parents had. To prevent this doubling from occurring in sexual reproduction, a special division process (meiosis) is…
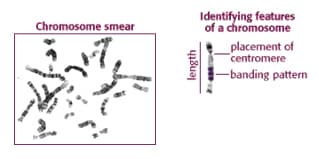
A karyotype is an organized profile of a person’s chromosomes. Chromosomes are arranged and numbered according to: – size, from largest to smallest – banding pattern, size and location of Giesma bands – centromere location, appear as a constriction This arrangement helps scientists quickly identify chromosomal alterations that may result in a genetic disorder. Karyotype…
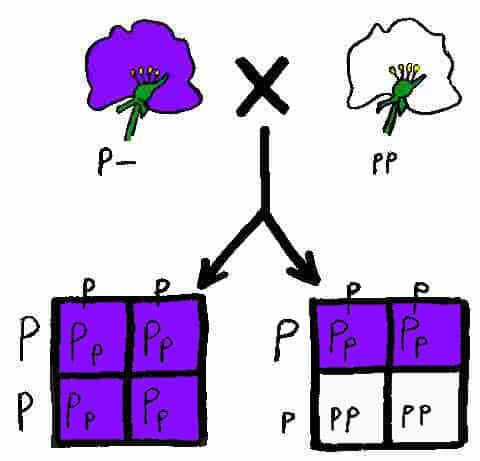
Gregor Mendel is considered the “father” of genetics because he offered the first significant insights into the mechanisms involved in the inheritance of biological traits. His discoveries were made during the mid 19th century. Mendel was a Moravian monk who spent several years at the University of Vienna studying science to become a high school…
Mutations – any change in a gene that is accompanied by a loss or change in the functioning of the genetic information; many mutations are harmful – spontaneous mutations have no known cause; improper crossing over, DNA replication – induced mutations are caused by mutagens; radiation, chemicals, viruses Somatic Mutations – occur in regular body…
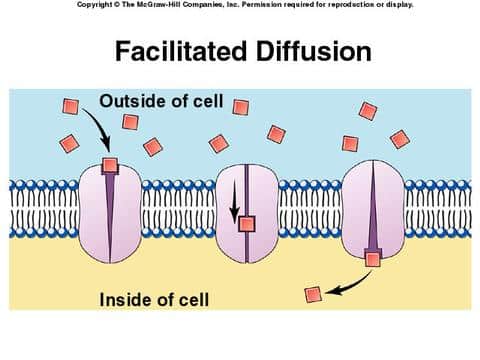
Facilitated Diffusion Allows diffusion of large, membrane insoluble compounds such as sugars (glucose) and amino acids Does not require energy (passive transport) Substance binds to membrane transport protein Molecules may enter the cell and leave the cell through the transport protein. Particles move from areas of high concentration to areas of low concentration; diffuse Active…
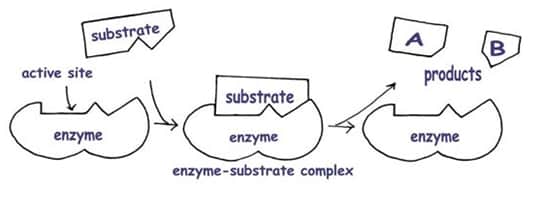
Enzymes are specialized proteins that speed up chemical reactions (biological catalysts) Without enzymes, cellular chemical reactions could not occur fast enough to maintain life. Enzyme Activity: – enzyme binds to the reactants, called the substrate(s), of a chemical reaction – the substrate joins with the enzyme at the enzymes active site forming an enzyme-substrate complex…
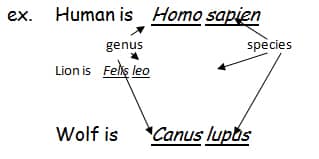
With the large diversity (variety) we need to sort or take inventory of everything (classify and name) classifying involves arranging living and nonliving things into groups which we can then study separately we also must give everything a name so that we can exchange information with others around the world. Naming Scientists have developed a…
Below is a table that compares the differences in cell structure between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Criteria Type of Cell Prokaryote Eukaryote Nucleus? No Yes Internal membranes? No (no organelles) Yes (membrane bound organelles) DNA Single chromosome; ring Many; linear Reproduction method Asexual (binary fission) Asexual and sexual Size Small 10 times as large as…
The table below lists the basic general characteristics that are used to differentiate between the different kingdoms. Criteria Kingdom Animals Plants Fungi Protists Archaebacteria Eubacteria Type of cells Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Prokaryotic Cell wall None Yes (cellulose) Yes (chitin) None Yes (peptidoglycan) Yes Cell organization Multicellular Multicellular Multicellular Single celled Single celled Single…
Matter makes up everything, everywhere. All matter, both living and non-living, is composed of miniature chemical building blocks called atoms. Your body contains billions of hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, phosphorus, sulfur and carbon atoms. What is life? What does it mean to be alive? How is something made “living”? There is no universal agreement on what…
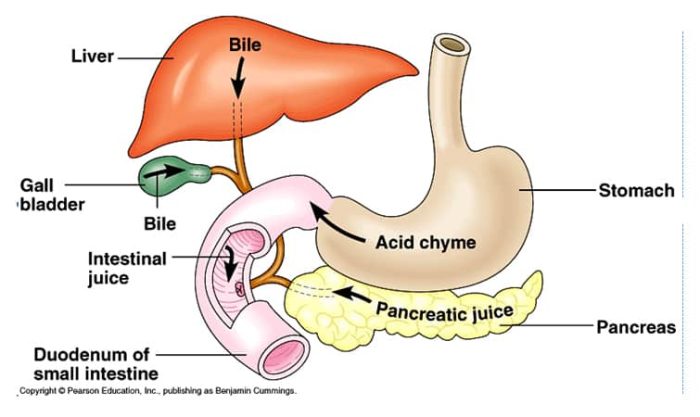
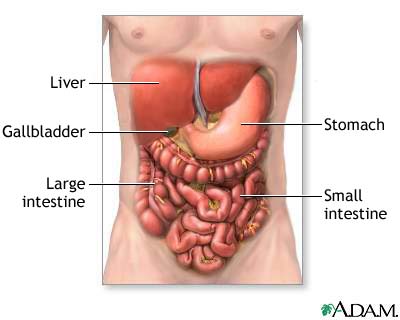
Liver – produces bile -bile emulsifies fats in the small intestine; increases surface area of fat particles Gall Bladder – stores bile between meals – releases bile when food moves into the small intestine Pancreas – manufactures and releases bicarbonate to neutralize acid coming out of the stomach – basic environment inactivates pepsin – releases…
Function of the Digestive System: To change foods you eat into chemical forms your body can use and eliminate anything that can not be used by your body. Food is typically in a form that is completely unsuitable for use by body cells. Food becomes useful only after it has been converted into smaller, simpler…