William completed his Bachelor of Science and Master of Arts in 2013. He current serves as a lecturer, tutor and freelance writer. In his spare time, he enjoys reading, walking his dog and parasailing.
Article last reviewed: 2022 | St. Rosemary Institution © 2010-2025 | Creative Commons 4.0
Common fungi: mushrooms, moulds, yeast and truffles 1. Cell Type: eukaryotic 2. Type of Reproduction: asexual and sexual life cycle Sex cell = spores – made by the sporangium – spores are spread by wind – spores germinate (grow) Asexual fragmentation may also occur 3. Characteristics nonmotile mycelium – vegetative part, under ground wide variety…
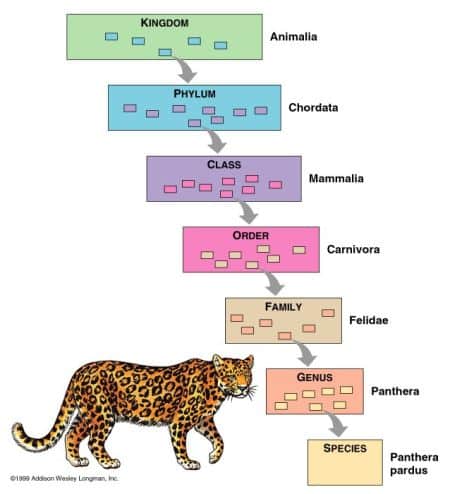
– the study of categorizing organisms Binomial Nomenclature – two-part scientific naming of organisms – the first word identifies the genus and the second word is the species Example: Ursus americanus – Ursus horribilis – Ursus arctos – Ursus maritimus – NOTE: the format: capitals and italics Levels of Classification (7) or Taxa: “King…
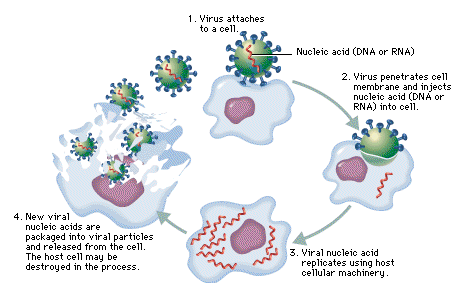
Four basic Steps: 1. Attachment and entrance: the virus recognizes the host cell and attaches. The whole virus or just it’s genetic material enters the cell. 2. Synthesis of proteins: The genetic material of the virus (DNA or RNA) instructs the cell to start making viral proteins and nucleic acids (DNA/RNA) 3. Assembly of a…
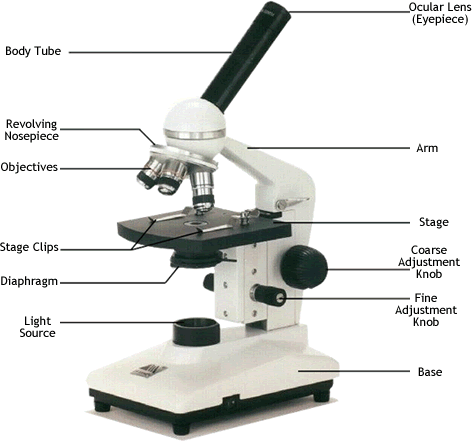
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM) -very expensive with 2 million times magnification – specimen must be cut very thinly and must be dead Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) – produces a 3-D image of the surface – whole specimen must be dead Compound Microscope – the one we use – two lenses illuminated by a light source…
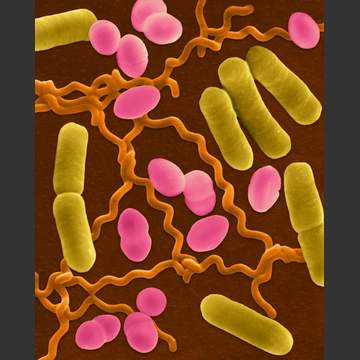
All Bacteria have the following characteristics: Unicellular and stick together in colonies Are prokaryotic (no nucleus, vacuoles, mitochondria or chloroplasts) They have a single chromosome in a DNA loop They reproduce asexually by binary fission Live in moist environment and are inactive in dry environments Two groups of Bacteria 1. Archaebacteria – primitive bacteria that…
He is the author of the novel, One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest (1962). An Academy award-winning film version of the novel was directed by Milos Forman in 1975, starring Jack Nicholson as the main character, McMurphy. Dale Wasserman wrote an adaptation of the novel which played on Broadway. Kirk Douglas had bought the right…
Economic Influence Economic Trends Domestic and International Trade Competitive Influence Market Structure Competitive Strategy Competitive Position Social and Demographic Influences Demographic Trends Multiculturalism Lifestyles Ecological Concerns Technological Influence Advances Research and Development Investment Information Technology Legal and Regulatory Influence Federal Laws/Regulations Provincial Laws/Regulations Self-regulation
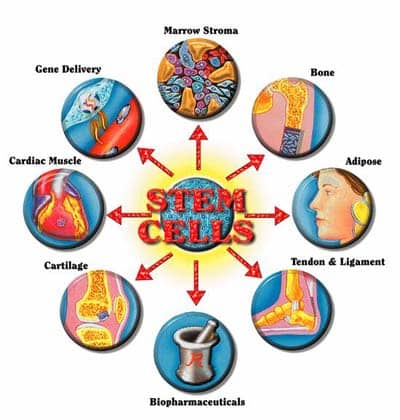
Organ Transplantation – Living donations of the kidney, part of liver, lobe of lung, part of intestine and portion of pancreas can be made – A donor must be healthy in order to give an organ – The demand for living organs is increasing – For cultural and personal reasons, some are resistant to transplants…
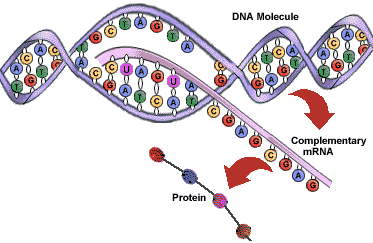
Initiation: – Upstream of the gene, RNA polymerase binds to a genes promoter region and unwinds the DNA double helix Elongation: – RNA polymerase starts building an mRNA, using the template strand of the DNA molecule, in the direction of 5’ to3’ – the strand that is not copied is called the coding strand – …
What Is a Real Hypothesis? A hypothesis is a tentative statement that proposes a possible explanation for some phenomenon or event. A useful hypothesis is a testable statement that may include a prediction. When Are Hypotheses Used? The keyword is testable. That is, you will perform a test of how two variables might be related.…
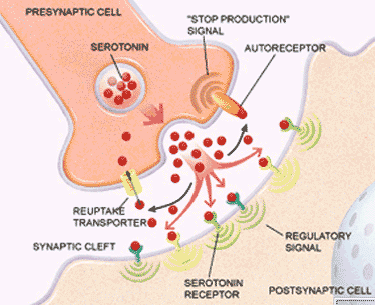
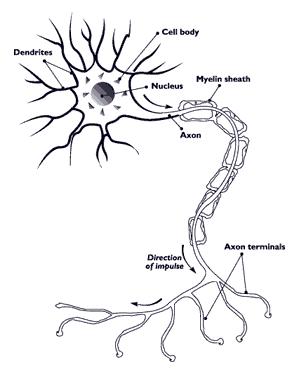
> synapse: spaces between neurons, or between neurons and effectors > vesicles containing chemical neurotransmitters are located at the end of neuron axons Electrical Signals: > electrical impulses moving along the axon stimulate the release of neurotransmitters Chemical Signals: > neurotransmitters are released from the presynaptic neuron and diffuse across the synaptic cleft > neurotransmitters…
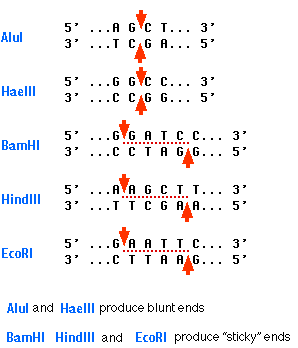
– obtained from bacterial cells where they act as an immune system, they digest foreign DNA molecules from viruses – molecular scissors that cut DNA at a specific base-pair sequence (the recognition site) – they scan DNA, stop at their recognition sites, then disrupt the phosphodiester bonds and the hydrogen bonds between nucleotides cutting a…
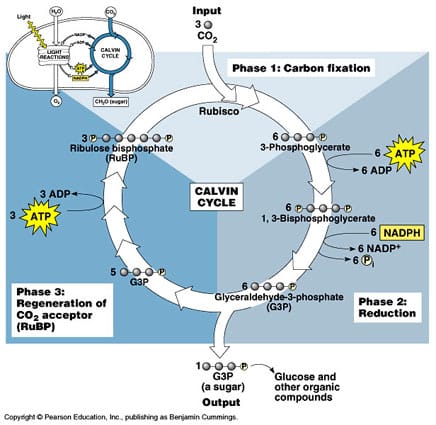
– cyclic process in the stroma that converts carbon dioxide into carbohydrate molecules – three phases: 1) carbon fixation, 2) reduction reaction, 3) RuBP regeneration Phase 1: Carbon Fixation – C02 added to RuBP -> unstable 6-carbon intermediate -> 2 3-carbon PGAs – required to occur three times, 3 CO2 + 3 RuBP -> 6…
Light Reactions: – require chlorophyll and take place in thykaloid membranes – absorb light energy and transfer it to ADP and NADP+ – energy is transferred to carbohydrate molecules in the Calvin cycle Carbon Fixation: – incorporate molecules of CO2(g) into organic molecules, such as glucose – require energy from ATP and NADPH – takes…
The nervous system is an elaborate communication system that functions to regulate the actions of your body to maintain the internal environment within safe limits Nerve Cells: Glial cells – non-neuronal cells that provide support and nutrition, maintain homeostasis, form myelin, and participate in signal transmission in the nervous system. Functions: – surround neurons and…
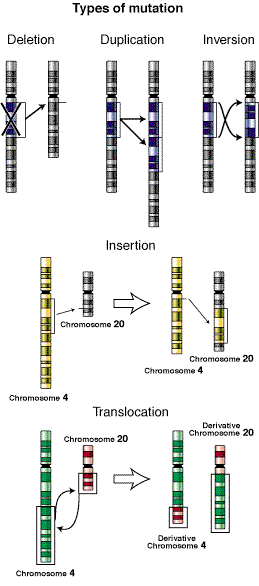
Mutations are errors made in the DNA sequence than can have negative side effects, no effect, or positive effects for an organism Point Mutations Mutations that occur at a certain point in the DNA Substitution – the replacement of one base in a DNA sequence by another base Deletion – the elimination of a base…
Thermoregulation is the maintenance of body temperature within a range that enables cells to function efficiently. Mammals, including humans, are endotherms, able to maintain a constant body temperature regardless of our surroundings. The hypothalamus acts as your body’s “thermostat”, detecting changes in body temperature and sending out messages to help restore the normal body temperature.…
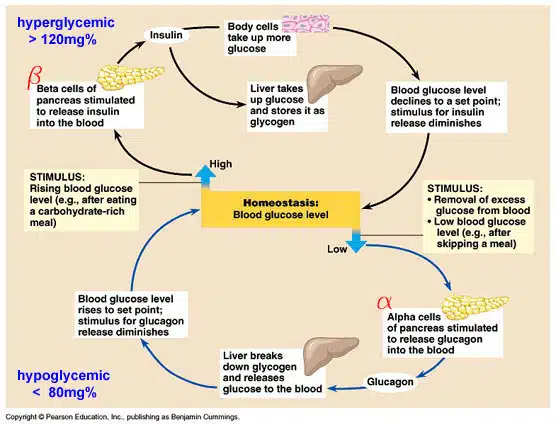
The human body works best at 37°C, with a 0.1% blood sugar level and a blood pH level of 7.35 The external environment and making demands on your body do not always provide the ideal conditions for life Your body must adjust these variations to maintain a stable internal environment Homeostasis is a term used…
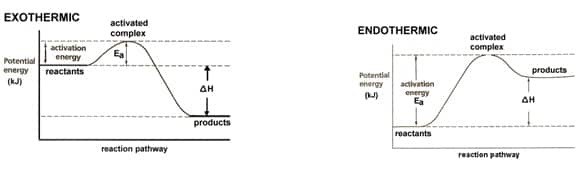
Living organisms must continually capture/acquire, store, and use energy to carry out the functions of life. Capturing/acquiring, storing and using energy are accomplished through cellular chemical processes. Cells are chemical machines that obey fundamental chemical and physical laws of nature. The sum of a cells chemical reactions is called metabolism. Energy Energy is the ability…
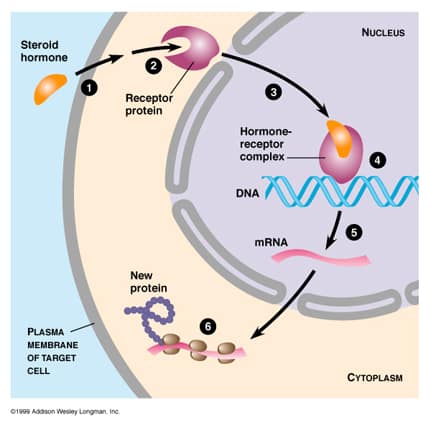
Function: ▪ synthesize and release hormones permitting them to act in concert and respond to changes in the body and maintain stability (homeostasis) ▪ Example organs – thyroid, pancreas (islets of Langerhans), adrenal glands, pituitary gland Tools: – hormones * chemicals released by cells in one part of the body that affect cells in other…